What vitamins do what? (helpful information!). Vitamins - description, classification and role of vitamins in human life. Daily requirement for vitamins Vitamins of the group in medicinal properties
National University physical culture and sports of Ukraine
Discipline: General biology Essay on the topic: "The influence of vitamins on the human body" Student 1st year 64 group Denisenko Sabina 26.10.2012. Kyiv 2012 Plan 1. Introduction 2. The effect of various vitamins on the human body 3. Conclusions 4. References 1. Introduction: The well-known word "vitamin" comes from the Latin "vita" - life. These various organic compounds received such a name not by chance: the role of vitamins in the life of the body is extremely large. Vitamins have the ability to increase the intensity of all physiological processes of the body, help in protecting it from the adverse effects of the external environment, increase resistance to infectious diseases, and during the period of illness contribute to a speedy recovery. Absence, deficiency, as well as oversaturation of the body with vitamins leads to a violation of a number of its most important functions. In winter, if it is irrational to approach the diet, the intake of vitamins usually drops sharply, which in turn can lead to spring beriberi. Compared to the main nutrients: proteins, fats, carbohydrates and mineral salts- vitamins are required by the body in very small quantities: from a few hundredths of a milligram per day, depending on the type of vitamin. But even in these small amounts, vitamins have a beneficial effect on metabolism, stimulate proper growth, development, have a positive effect on the general condition, increase resistance to various diseases, strengthen muscle, bone, circulatory and other systems, and they act interrelatedly. Currently, about 20 different vitamins are known. And if the benefits of vitamins obtained artificially are disputed by many, then vitamins of natural origin, contained, for example, in plant foods, are not in doubt by almost anyone. We give a list of only some vitamins, consider their effect on the body, and also give as an example food products containing these useful elements.
2. The effect of various vitamins on the human body Vitamin A has an effect on human growth, improves skin condition, contributes to the body's resistance to infection. Vitamin A is found in mountain ash, apricots, rose hips, black currants, sea buckthorn, yellow pumpkins, watermelons, red peppers, spinach, cabbage, celery tops, parsley, dill, watercress, carrots, sorrel, green onions, green peppers, nettles, dandelions, clover, as well as in animal products (fish oil, milk fat, butter, cream, cottage cheese, cheese, egg yolk, liver fat and other fats). organs (heart, brain). Vitamin B1 It has a positive effect on the functions of muscles and the nervous system, is part of the enzymes that regulate many important functions of the body, and is involved in metabolism. B1 is found mainly in products of plant origin: in cereals, cereals (oats, buckwheat, millet), in wholemeal flour (with fine grinding, the part of the grain richest in vitamin B1 is removed with bran, therefore, in higher grades flour and bread, the content of vitamin B1 is sharply reduced). Especially a lot of vitamin in grain sprouts, in bran, in legumes. Also found in hazelnuts, walnuts, almonds, apricots, rose hips, red beets, carrots, radishes, onions, watercress, cabbage, spinach, potatoes. There is in milk, meat, eggs, yeast. Vitamin B2 affects the growth and renewal of cells, is part of many enzymes necessary for the body. Important for maintaining vision. There is a lot of B2 in legumes, spinach, rose hips, apricots, leafy vegetables, vegetable tops, cabbage, tomatoes. It is also found in animal products: liver, milk, eggs, yeast.
Vitamin VZ affects the overall metabolism and is involved in the formation of enzymes that ensure the digestion of food. A lot of OT is found in legumes (beans, peas, beans), mushrooms (champignons, porcini), fresh vegetables (red beets, asparagus, cauliflower). Present in dairy and dairy products. The liver, kidneys, meat, fish, and eggs are also rich in this vitamin.
Vitamin B6 important for the life of the body, is involved in metabolism. It is necessary for recovery from past illnesses and the use of antibiotics. Vitamin deficiency negatively affects the functions of the brain, blood, leads to disruption of the blood vessels, leads to the occurrence of dermatitis, diathesis and other skin diseases, and disrupts the functions of the nervous system. Especially a lot of vitamin B6 is found in cereal sprouts, walnuts and hazelnuts, spinach, potatoes, cauliflower, carrots, lettuce, cabbage, tomatoes, strawberries, cherries, oranges and lemons. It is also found in meat products, fish, eggs, cereals and legumes.
Vitamin B12 affects blood formation, activates the processes of blood coagulation, participates in the formation of substances necessary for the body, activates the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. It has a beneficial effect on the functions of the liver, nervous and digestive systems. The main source of this vitamin are food products of animal origin: beef liver, fish, seafood, meat, milk, cheeses. Also, vitamin B12 in humans is synthesized in the intestine.
Vitamin C increases the body's defenses, limits the possibility of respiratory diseases, improves the elasticity of blood vessels (normalizes capillary permeability). Vitamin has a beneficial effect on the functions of the central nervous system, stimulates the activity of the endocrine glands, promotes better absorption of iron and normal hematopoiesis, and prevents the formation of carcinogens. Contained in fresh plants: wild rose, dogwood, black currant, mountain ash, sea buckthorn, citrus fruits, red pepper, horseradish, parsley, green onions, dill, watercress, red cabbage, potatoes, rutabaga, cabbage, in vegetable tops. In medicinal plants: nettle, boudre, lovage, forest fruits.
Vitamin D ensures normal growth and development of bones, promotes the deposition of calcium in bone tissue. Vitamin D helps in the fight against rickets, increases the body's resistance. The formation of vitamin D is facilitated by ultraviolet rays. The need for vitamin D in adults is satisfied by its formation in human skin under the influence of ultraviolet rays and partly by its intake with food. Vitamin D is found in some fish products: fish oil, cod liver, Atlantic herring, notothenia. And also they are rich in alfalfa, horsetail, nettle, parsley, mushrooms.
Vitamin E promotes the absorption of proteins and fats, participates in the processes of tissue respiration, affects the functioning of the brain, blood, nerves, muscles, improves wound healing, delays aging. Vitamin E is found in almost all foods, but it is especially abundant in cereals and bean sprouts (wheat and rye sprouts, peas), in vegetables - asparagus, tomatoes, lettuce, peas, spinach, parsley tops, rosehip seeds. Some quantities are found in meat, fat, eggs, milk, beef liver.
Vitamin K essential for normal blood clotting. Vegans who eat leafy greens daily with some fat are getting even more vitamin K than they need. Even those who don't can get enough vitamin K from gut bacteria, unless people are on a long course of antibiotics. The best source of vitamin K is leafy greens. Consuming it in sufficient quantities, you can be sure of meeting the daily requirement for this vitamin. Vitamin P is a natural compound that combines a group of biologically active substances called flavonoids. It includes about 150 elements: hesperidin, esculin, anthocyanin, catechin and so on. Due to the fact that vitamin P can partially cover the body's need for vitamin C, it was given the additional name vitamin C2 or C-complex. But its more common, although not entirely accurate, name is "rutin", since rutin is just one of many substances belonging to the flavonoid group.
Vitamin P owes its discovery to the American biochemist of Hungarian origin Albert Szent-Györgyi. In 1936
he managed to isolate a certain substance from the lemon peel, the effect of which had a positive effect on patients with hemorrhagic diathesis and on guinea pigs infected with scurvy. The name of the element comes from the first letter of the term "permeability", which means permeability, since it is the decrease in vascular permeability that is the fundamental characteristic for vitamin P.
Vitamin P (routine) health benefits
Vitamin P refers to substances that the human body is not able to produce itself. Therefore, it is of particular value to him. Regular use of vitamin P normalizes the condition of the capillary walls, increasing their strength and elasticity, lowers blood pressure, slows down the heart rate. It is believed that daily use of rutin in an amount of 60 mg can reduce intraocular pressure. True, in this case, the prophylactic course should be at least four weeks. Vitamin P is also involved in bile formation, helps regulate the daily rate of urine output and gently stimulates the function of the adrenal cortex. It inhibits the production of histamine and serotonin, has anti-edematous and analgesic effects. Thus, vitamin P facilitates and accelerates the course of allergic reactions, in particular bronchial asthma.
3. Conclusions The uniqueness of vitamins of natural origin lies in the fact that the possibility of hypervitaminosis when consuming plant products or animal products is negligible. The optimal vitamin balance in the body is the key to good health and beauty. Diversify your menu with fresh products, combine them, and spend more time in the air and sunlight and beriberi will bypass you! Vitamins for our health.
If biological substances do not constantly enter your body, then protein compounds and irritating cholesterol accumulate in the subcutaneous layer, and form a crust that leads to wrinkles and bruises. Vitamins A, C, E give us the so-called fire and at the same time create a seductive and radiant delight. What our teeth really need is calcium and vitamin C. Your gums will stop bleeding if you drink the juice of one lemon every day. The first step towards rejuvenation and in order to look good in age is vitamin C, which takes part in the fat moisturizing of the external environment in the cells of the body, and therefore protects vitamin A and carotene. Vitamins and other biological substances make us not only healthy, active, cheerful and pleasant. With their help, you can lose weight without a diet. A lover of eating meat and poultry at night will not gain more than 30 grams in weight if he eats it with lemon. Who wants to lose weight should eat a lot of carbohydrates and always in a healthy form: fruits, vegetables, potatoes, rice, etc. Despair, depression, fear, disturbed sleep, forgetfulness and instant fatigue respond to insufficient intake of vitamins. Often only one meal that contains many vitamins can improve the nervous state. Without such important vitamins, there is pain in the stomach, intestinal upset, palpitations, dizziness, difficulty urinating, as well as breathing, and the nervous system is depleted. Nutrilight offers us all vital vitamins, solving the vital problem of proper human nutrition and health. Having made an analysis of what I wrote about, I can say once again about the healing effect of vitamins: youth, vitality, nutrition of the body, healthy sleep, and so on. Vitamins are very important especially during adolescence. They are especially important in exams, they help not to overload and relieve stress and fear, that is, keep you in shape. That's all about the miracle drug called vitamin.
4. References
1.Vakulenko V.V. The healing power of vitamins and minerals. -Rostov n/D.: Phoenix, 2005.- 320s. 2. Biology for university applicants / A.G. Mustafin, F.K. Lakgueva, N.G. Bystrenina, etc.: Ed. V.N. Yarygin. – M.: Vysh. school, 1995.-478 p.
3. Popov S.V. Valeology at school and at home: On the physical well-being of schoolchildren. St. Petersburg: union, 1997.-256 p.
Group B includes eight vitamins:
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine);
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin);
- Vitamin B3 (niacin, vitamin PP, nicotinic acid);
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid);
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine, pyridoxal, or pyridoxamine);
- Vitamin B7 (biotin, vitamin H);
- Vitamin B9 (folic acid, folates, vitamin M, vitamin Bc);
- Vitamin B12 (cobalamin, cyanocobalamin).
Vitamin-like substances
These substances are not included in the list of the main ones, since they are either produced by our body or are not vital. Their list:
- (choline, adenine);
- (inositol);
- B10 (para-aminobenzoic acid, H1);
- B11 (carnitine);
- B13 (orotic acid);
- B15 (pangamic acid);
- B17 (laetral).
Interaction of vitamin B1 with other substances
- When interacting with sulfites or nicotinic acid (for example, when several drugs are combined in one syringe), thiamine is completely destroyed.
- Thiamine destroys the antibiotics benzylpenicillin and streptomycin, so their simultaneous administration is unacceptable.
- Despite the great popularity of complex preparations (such as Milgamma or Kombilipen), it is not recommended to administer vitamins B1 and B12 in one injection. The fact is that pyridoxine slows down the conversion of thiamine into its biologically active form, and cyanocobalamin increases the risk of developing allergic reactions to thiamine.
- Thiamine weakens the effect of the muscle relaxant suxamethonium iodide and Ditilin.
- Ethanol slows down the absorption of vitamin B1.
- It is not recommended to mix thiamine with alkaline and neutral solutions, carbonates, citrates and barbiturates, with sodium hydrosulfite. In such combinations, the chemical structure of vitamin B1 becomes unstable.
Now you know everything about vitamin B1 (thiamine) - an extremely important chemical compound, without which life is impossible. Eat a varied diet, eat nuts and legumes, then you will never be affected by vitamin B1 deficiency, and the nervous and cardiovascular systems will remain highly efficient!
5 / 5 (13 votes)
daily requirement
The daily requirement of a person for vitamins varies depending on many factors: age, gender, health status, physical activity. It is important to satisfy the need for vitamins, since vitamin deficiency can cause great harm, undermining the proper functioning of organs and systems. Hypervitaminosis is no less dangerous - an excess of vitamins can cause many problems.
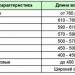
Table. The average daily human need for B vitamins
The need for vitamins of the group under consideration is increasing(but not higher than the upper allowable rate indicated in the table) with factors:
- increased physical activity;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding;
- elderly age;
- diets limited to foods containing B vitamins;
- drinking alcohol, smoking;
- stress, depression;
- drinking a lot of coffee and tea;
- chronic diarrhea;
- the use of a considerable amount of sugar, sweets.
Why do women need vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 is involved in many internal processes. Cyanocobalamin prevents fat cells from accumulating in the liver, protects against obesity, stimulates the active activity of leukocytes.
The daily dosage for women is 3 mcg, and nursing mothers should take no more than 4 mcg.
Vitamin-mineral complexes will help to fill the body's daily need for microelements. Vitamin B12 regulates the emotional state and brain activity.

The following advantages can be distinguished:
- Help in the treatment of depression.
- Improvement and normalization of sleep.
- Increased blood circulation, quick adaptation to a sharp change in the regime of the day.
- Vitamin contributes to the protection of nerve fibers from severe stress and excessive overexertion.
- Aid in the normal absorption of amino acids.
- Stimulation of bone formation, therefore, B12 vitamins are recommended to be taken in adolescence.
Note! Each person who takes vitamin-mineral complexes must comply with the established dosage.
An excessive amount of vitamin B12 in the body leads to urticaria, thrombosis, heart failure, and pulmonary edema.
It dissolves well in liquid, so negative symptoms are easily removed.
Food Sources of B Vitamins
Proper, varied nutrition- the key to an adequate supply of the body with useful B vitamins.
Do not forget that many "B" components lose their properties or disappear during technical, thermal and other food processing. And also if they are stored incorrectly. Hence, an adjustment is required to draw up the need for products in order to obtain the daily requirement of vitamins.
Table. Sources of B group vitamins. Most Common Products
| Vitamin name | Products | Quantity in 100 g | % of the average daily norm |
| Vitamin B1 (thiamine) | sunflower seeds | 1.8 mg | 120 |
| Flax seeds | 1.6 mg | 106 | |
| Pork, tenderloin | 1.4 mg | 93 | |
| Soy, peas, pistachios | 0.9 mg | 60 | |
| Wheat bran, peanuts, hazelnuts | 0.7 mg | 46 | |
| Liver: duck, goose, chicken. Rye bran, pink salmon caviar, lentils, beans, oat groats, buckwheat | 0.5 mg | 33 | |
| Beef and lamb kidneys, beef and pork heart, beef and pork liver, trout, chum salmon, kelp | 0.3 mg | 20 | |
| Green peas, almonds, catfish, navaga, salmon, pink salmon | 0.2 mg | 13 | |
| Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | Liver: pork, beef, lamb, chicken. Lamb and beef kidneys | 2 mg | 111 |
| Pork kidneys | 1.5 mg | 83 | |
| Chicken heart, goose and duck liver, wheat germ flour | 0.9 mg | 50 | |
| Quail egg, chicken egg white, almonds | 0.7 mg | 38 | |
| Laminaria, champignons, chicken egg | 0.5 mg | 27 | |
| White mushroom, oyster mushroom, turkey meat, trout, herring, cheese and homemade cottage cheese | 0.3 mg | 16 | |
| Spinach, cottage cheese, yogurt, Brussels sprouts, sunflower seeds | 0.2 mg | 11 | |
| Kefir, milk, fermented baked milk, oysters, walnuts, whole grain flour | 0.15 mg | 8 | |
| Vitamin B3 (niacin) | Pork liver, peanuts | 17 mg | 85 |
| Tuna, broiler chicken liver, sunflower seeds | 15 mg | 75 | |
| Turkey, wheat bran, chicken liver, chicken, turkey | 13 mg | 65 | |
| Rabbit meat, mackerel, pork kidneys, horse mackerel | 11 mg | 55 | |
| Salmon, chum salmon | 9 mg | 45 | |
| Pink salmon, lamb, goose and duck liver, sunflower seeds | 8 mg | 40 | |
| Champignons, blue whiting, oyster mushroom, trout, carp, dried apricots, almonds | 5 mg | 25 | |
| Brussels sprouts, spinach, asparagus, dill, green pea, avocado, celery, bell pepper, green peas | 1.5 mg | 8 | |
| Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) | Liver: pork, beef, duck, goose, lamb. Laminaria (dried) | 6 mg | 120 |
| Beef kidneys, egg yolk, pork kidneys, white mushroom | 3.5 mg | 70 | |
| Heart: beef, pork, lamb. Peas, wheat bran, champignons, trout | 2.6 mg | 52 | |
| Quail egg, chicken, trout, salmon | 1.65 mg | 33 | |
| Turkey, chicken egg, oyster mushroom | 1.3 mg | 26 | |
| Tuna, veal, chum salmon, sunflower and flax seeds | 1 mg | 20 | |
| Cauliflower, broccoli, green peas, yogurt, bran bread | 0.8 mg | 16 | |
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | pistachios | 1.7 mg | 85 |
| Garlic greens, wheat bran, chicken, sunflower seeds | 1.3 mg | 65 | |
| Lamb and chicken liver, beans, soy | 0.9 mg | 45 | |
| Salmon, mackerel, tuna, broiler chicken liver, goose and duck liver | 0.8 mg | 40 | |
| Beef liver, sardine | 0.7 mg | 35 | |
| Tomato paste, pink salmon, chicken | 0.6 mg | 30 | |
| Pork kidneys and liver, beef kidneys, chum salmon, pork, sprat, turkey, pomegranate, rabbit meat, chickpeas, herring, flax seeds | 0.5 mg | 25 | |
| Veal, beef, bananas, bell peppers, trout, catfish | 0.35 mg | 17 | |
| Potato, Brussels sprouts, avocado | 0.3 mg | 15 | |
| Vitamin B7 (biotin) | sunflower seeds | 670 mcg | 1300 |
| Pork kidneys | 140 mcg | 280 | |
| Beef liver and kidneys | 90 mcg | 180 | |
| Pork liver, hazelnut | 80 mcg | 160 | |
| soy, egg yolk | 60 mcg | 120 | |
| Peanut | 40 mcg | 80 | |
| Laminaria, corn, oatmeal, chicken egg, peas, walnut | 20 mcg | 40 | |
| Almonds, mushrooms | 16 mcg | 32 | |
| Cheese, cottage cheese, persimmon, millet | 7 mcg | 14 | |
| Vitamin B9 (folic acid) | Liver goose and duck, | 730 mcg | 182 |
| chickpeas | 550 mcg | 137 | |
| Beans | 450 mcg | 112 | |
| Beef and chicken liver, peanuts | 240 mcg | 60 | |
| Lamb and pork liver, sunflower seeds | 230 mcg | 57 | |
| Soya | 200 mcg | 50 | |
| Hazelnut, parsley, cod liver | 110 mcg | 27 | |
| Walnut, beans, lentils, flax seeds | 90 mcg | 22 | |
| Avocado, spinach, beets, savoy and Chinese cabbage, wheat bran, walnut, broccoli | 80 mcg | 20 | |
| Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) | Lamb liver | 90 mcg | 3000 |
| Liver: beef, goose, duck | 55 mcg | 1830 | |
| Pork liver | 30 mcg | 1000 | |
| Beef kidneys | 25 mcg | 830 | |
| Chicken liver, oysters, pork kidneys | 16 mcg | 530 | |
| Herring, mussels, mackerel, sardine, tuna | 11 mcg | 366 | |
| Rabbit meat, chum salmon, pink salmon, trout | 5 mcg | 160 |
As you can see from the table, a lot of B vitamins are found in the same products. To get all the valuable B vitamins, you need to include in your diet ingredients such as:
- Offal: liver, kidneys, heart;
- Meat: pork, veal, beef, lamb, rabbit meat;
- Fish: trout, salmon, pink salmon, tuna, herring, trout, carp;
- Seeds: sunflower, flax, sesame;
- Nuts: peanuts, almonds, walnuts;
- Cereals: soybeans, peas, beans, millet, oatmeal, lentils;
- Fruits and vegetables: persimmon, avocado, green garlic, parsley, spinach;
- And also: kelp, eggs, cheese, cottage cheese, yogurt, fermented baked milk.
Recipes for foods fortified with thiamine

Taking into account the constant need of the body for the B1 compound, hypovitaminosis can be avoided by including foods containing a large amount of a water-soluble substance in the daily diet.
Consider recipes for dishes that can be easily prepared "on hastily» at home. At the same time, they will not only be tasty and nutritious, but will also help fill the lack of thiamine in the body.
Smoothie "Firstborn"
Ingredients:
- cream with a fat content of 10% - 100 ml;
- honeysuckle - 200g;
- honey - 15 ml;
- ice (snow) - 50 g;
- mint (melissa, pepper).
Preparation description:
- Rinse honeysuckle berries, grind in a blender.
- Add honey, mint, cream, ice to the resulting mixture. Whisk all ingredients.
- Pour a fortified drink into a glass.
- When serving, garnish the smoothie with mint and a slice of lemon.
Warm salad with pine nuts
Ingredients:
- olive oil - 60 ml;
- lemon peel - 5 g;
- lemon juice - 15 ml;
- cherry tomatoes - 250 g;
- zucchini - 1 pc;
- sunflower seeds - 100 g;
- pine nuts - 100 g;
- soft feta cheese - 200 g;
- parsley - a bunch;
- mint;
- salt;
- pepper;
- lettuce leaves.
Cooking technology:
- Line a baking sheet with paper, which, in turn, needs to be greased with oil.
- Cut the zucchini into circles, salt, pepper, put in a baking dish. The thickness of the vegetable should not exceed 5 mm.
- Place a baking sheet with zucchini in a preheated oven for 15 minutes, maintaining the temperature in the oven at 180 degrees.
- Cut mint, parsley, cheese, tomatoes.
- Prepare the dressing. To do this, combine and beat the following products: salt, pepper, olive oil, zest, lemon juice.
- Remove the toasted zucchini from the oven. Put them in a salad bowl, add chopped cherry tomatoes, herbs, cheese, sunflower seeds, pour dressing, mix.
- Serve the dish in portions. To do this, put lettuce leaves on a plate, pour warm salad on them, sprinkle with pine nuts on top.
Vegetarian mediterranean salad
Ingredients:
- cauliflower - 500 g;
- bell pepper - 1 pc;
- brown rice - 200 g;
- pine nuts - 50 g;
- almonds - 50 g;
- onion - 1 pc;
- dried cranberries - 100 g;
- sesame seeds - 30 g;
- lemon juice - 40 ml;
- olive oil - 50 ml;
- salt;
- pepper.
Cooking sequence:
- Rinse rice, boil (do not cool).
- Onion, sweet pepper cut into strips.
- Divide the cabbage into inflorescences, boil, discard in another shlag.
- Rinse the cranberries, pour boiling water for 2 minutes, dry on a paper towel.
- Combine all salad ingredients, salt, pepper, season with olive oil and lemon juice.
- Serve the dish so that the rice in the salad is warm.
Top Content of the Month
- Why You Can't Diet Yourself
- 21 tips on how not to buy stale food
- How to keep vegetables and fruits fresh: simple tricks
- How to kill cravings for sweets: 7 unexpected products
- Scientists say youth can be extended
Useful properties and signs of shortage
B vitamins are responsible for the proper functioning of the nervous system, they reduce the negative impact of stressful situations. In addition, the compounds regulate metabolism, normalize blood sugar levels. Maintain muscle and skin tone. The immune system also needs to be supported by vitamins of this group. The components of the group improve the functioning of the cardiovascular and digestive systems.
The key role of B vitamins is to maintain cell health. With a lack of nutrients, they are depleted and eventually die. A group of vitamins regulates the formation of new cells. They are not allowed to randomly divide, which can lead to serious consequences in the form of the formation of cancer cells.
Thiamine (B1)
Thiamine, a vitamin of good mood and optimism is necessary for:
- nervous system,
- energy and carbohydrate metabolism,
- cell energy,
- of cardio-vascular system,
- digestive processes.
Signs of a vitamin deficiency:
- Irritability, depression, poor sleep, fatigue,
- Disorders of the cardiovascular system, shortness of breath,
- Digestive problems: constipation, lack of appetite.
Riboflavin (B2)
Riboflavin, the life energy vitamin, is essential for:
- skin,
- mucous membranes,
- hair and nails
- carbohydrate and fat metabolism,
- cellular respiration and energy,
- good vision,
- growth and muscle mass.
Riboflavin deficiency symptoms can include:
- hair loss,
- peeling of the skin on the face,
- pain in the eyes, increased photosensitivity,
- inflammation of the tongue
- small cracks on the lips.
Niacin (B3)
Niacin, lifeguard nerve cells needed for:
- nervous system,
- gastrointestinal tract,
- skin,
- carbohydrate, protein, fat metabolism,
- respiration and cell energy,
- good mood and sleep,
- of cardio-vascular system,
- maintaining normal cholesterol levels
- muscles and connective tissues.
Deficiency symptoms:
- depression, fatigue, poor sleep, distraction,
- skin diseases,
- mouth ulcers, gum sensitivity,
- poor appetite, nausea, diarrhea,
- headache.
Pantothenic acid (B5)
Vitamin participant of metabolism is necessary for:
- health of the skin, hair and mucous membranes,
- prevention of inflammation processes,
- normal blood circulation
- attention concentration,
- slenderness and vigor,
- prevent early aging and wrinkles.
Deficiency signs:
- joint pain,
- blurred vision,
- cracks in the corners of the mouth,
- irritability, depression,
- memory impairment,
- convulsions,
- hair loss,
- dermatitis, eczema,
- constipation, digestive problems,
- headaches, weakness, fatigue.
Pyridoxine (B6)
Vitamin of health and immunity is necessary for:
- strong immunity,
- formation of gastric juice,
- good vision,
- cardiovascular system and blood circulation,
- normal hair growth
- muscle activity,
- nervous system,
- protein digestion,
- carbohydrate and fat metabolism.
Deficiency symptoms:
- decreased appetite,
- violation of the condition of the skin,
- fatigue, muscle weakness,
- irritability, depression,
- cracks in the corners of the mouth,
- hair loss,
- limb numbness,
- arthritis, circulatory disorders.
Biotin (B7)
Skin and hair health vitamin is essential for:
- synthesis of fats and glycogen,
- carbohydrate metabolism,
- skin, nails, hair,
- muscle and nerve cells.
Deficiency signs:
- violation of the normal condition of the skin,
- irritability, depression, depression,
- oily or dry skin
- hair loss,
- gray color of the mucous membranes of the larynx and mouth,
- muscle pain.
Folic acid (B9)
The Good Mood Vitamin is essential for:
- normal growth and division of cells,
- pregnant women for: proper development and bearing of the fetus,
- cardiovascular health,
- nervous system,
- workings of hydrochloric acid and good appetite
- proper functioning of the liver and gastrointestinal tract,
- hair health,
- brain work.
Signs of a folate deficiency:
- in pregnant women: prematurity of the fetus and developmental disorders of the child,
- anxiety, distraction, insomnia, forgetfulness, fear, fatigue,
- inflammation of the tongue, mucous membrane of the lips,
- anemia,
- digestive disorders,
- growth and development disorders.
Cobalamin (B12)
The most amazing and important vitamin is needed for:
- proper functioning of the nervous system, as well as the brain,
- good mood and optimism,
- muscle activity,
- energy metabolism, fat digestion,
- normal growth and development,
- metabolism, conversion of amino acids.
B12 and B9 are interconnected vitamins, they together participate in hematopoiesis.
Cobalamin deficiency symptoms:
- nervousness, irritability, depression,
- fatigue, difficulty moving,
- limb numbness,
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity,
- painful menstruation,
- anemia, leukopenia.
Application
Many argue that, due to the fact that this vitamin complex plays a key role in converting food into energy and its effect on the body is great, it will be useful in a variety of situations, including anxiety, depression, heart disease and premenstrual syndrome (PMS). ).
In addition, some people take it to improve tone, improve mood and memory, improve skin and hair health, and to stimulate the immune system - these are the reasons why such vitamins are prescribed.
Most people who make sure their diet is rich and varied get enough vitamin B from food, but there are those who may not get enough, in particular those over 50 who take antacids, suffer from celiac disease, the disease Crohn's, gastritis or other digestive disorders - they drink vitamins separately.
If you've had fat removal or stomach surgery, drink alcohol regularly, or follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, you're at risk for a deficiency in this life-sustaining vitamin.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women may need more vitamins B6, B12 and folic acid - what they are for is very important for the formation of the fetus and in the first years of life.
Vitamin B deficiency
The symptoms of vitamin deficiency were discussed above separately. The following symptoms may indicate a lack of all components of group B:
- Problems with the nervous system, depression, bad mood, irritability, insomnia.
- Violation of the condition of the skin.
- Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth and lips.
- Visual impairment.
- Digestive problems.
- Limb numbness, muscle atrophy.
- Breathing becomes difficult and the heartbeat quickens, in some cases dizziness is noted.
- In addition, a lack of vitamin B can cause thinning and hair loss.
- Patients become more sensitive to light.
- Cholesterol rises to dangerous levels.
Vitamin B1 deficiency
In developed countries, vitamin B1 deficiency is rare, as people have the opportunity to eat a varied diet and consume at least a small amount of thiamine-rich foods. However, with prolonged adherence to strict diets, thiamine reserves run out, which leads to the appearance of hypovitaminosis B1 with characteristic symptoms.
- Beriberi disease (described at the beginning of the article);
- Korsakov-Wernicke syndrome (Gaye-Wernicke);
- Weakness and muscle atrophy up to cuts and paralysis;
- Inflammation of nerve fibers and a decrease in mental activity, memory loss, orientation disorders in space and time, visual disturbances;
- Digestive disorders and the appearance of ulcerative-erosive lesions on the mucous membranes.
- Violations of the heart and blood vessels up to the development of heart failure.
- The appearance of neurodermatological diseases such as psoriasis or eczema.
Excess B vitamins in the body
Dangerous and excess substances. With abnormal ingestion of B vitamins, intoxication begins. Excess compounds can cause allergies. The most dangerous and harmful, with excessive use, are substances B3, B6 And B9(upper allowable norms indicated in the table of average daily norms, above) as they can cause disorders in the functions of the liver and gallbladder.
Manifestations are similar in nature to the symptoms of hypovitaminosis. Headaches, disorders of the vestibular apparatus, intestinal disorders, convulsions, numbness and insomnia are possible.
Signs and causes of vitamin deficiency in the body

The daily norm of thiamine for a child is 0.5 - 1.7 milligrams, for women - 1.3 - 2.2, for men - 1.6 - 2.5.
During pregnancy, for the full formation of the fetus, the need for vitamin B1 increases and reaches 2.5 milligrams per day. The lack of a useful compound in the body carries a potential threat of improper laying of organs and the appearance of deviations in the work of the central nervous system of the unborn baby. A woman feels a thiamine deficiency especially painfully in the third trimester, when there is severe pain in the hips, lower back, due to the pressure of the uterus on the nerve plexuses. Therefore, it is important to ensure that a pregnant woman systematically compensates for the lack of a vitamin, consumes foods rich in the “hormone of happiness” daily.
Definition of hypovitaminosis B1
Primary symptoms:
- numbness of hands, feet;
- dysfunction of the brain;
- increased irritability, tearfulness, feeling of anxiety;
- chilliness, even at 25 degrees Celsius;
- Wernicke-Korsakov syndrome (observed in patients suffering from alcohol dependence);
- memory loss;
- increased fatigue;
- hand trembling;
- insomnia;
- headache;
- depression;
- feeling of depression;
- muscle weakness;
- deterioration in coordination;
- diarrhea;
- an increase in the size of the liver;
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- nausea;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- burning in the epigastric region;
- constipation;
- arterial hypotension;
- cardiopalmus;
- unstable, rapid pulse;
- shortness of breath with little exertion;
- acute heart failure;
- tachycardia.
In the complete absence of thiamine, a serious disease “take-take” occurs: harmful acids (lactic, pyruvic) accumulate in the body, carbohydrate metabolism is disturbed, the heart muscle, nervous system, and digestive tract are affected. There comes a sharp exhaustion, anorexia.
In view of the fact that the nutrient is not able to accumulate in the body, it is important to constantly replenish its reserves, otherwise beriberi gradually sets in.
Causes of vitamin B1 deficiency
- Regular coffee intake. Daily consumption of a caffeinated drink results in the release of large amounts of hydrochloric acid, which destroys 50% of thiamine in the body.
- Removal of coarse fiber (bran) from vegetable raw materials. Products "poor" in thiamine - polished rice, white bread, "extra" oatmeal, bleached grains.
- Consumption of refined carbohydrate foods (bakery and confectionery, rich pastries, pasta). Regular intake of such products increases thiamine deficiency by 3 times.
- Prolonged heat treatment of food. If food is cooked at a temperature of 200 degrees for 45 minutes, the loss of active thiamine reaches 50%.
- Preservation of vegetables and fruits. Sterilization of products, for 20 minutes, leads to the loss of 25% of the vitamin.
- Profuse sweating.
- The presence of chronic infectious diseases.
- Pregnancy. In the last trimester, a woman's need for a nutrient increases by 2 times. Therefore, for expectant mothers, the daily dosage of thiamine should be 3 milligrams.
- Excessive heating or hypothermia of the body.
Thiamine deficiency for a long time (more than a year) leads to disruption of BJU metabolism and a decrease in the rate of formation of a cellular energy source. This means that the glucose received with food is not able to transform into an ATP molecule, as a result, toxic products of incomplete carbohydrate processing (pyruvate, lactic acid) accumulate in the blood. These metabolites, penetrating the tissues of the brain and spinal cord, disrupt their proper functioning and provoke the development of neurological diseases. Timely identification and elimination of factors contributing to the deficiency of water-soluble vitamin in the body will help prevent the risk of such disorders.
Harmful properties of group vitamins
The main problem that can be encountered when using B vitamins is the lack of complexity. It is important to maintain a vitamin balance without neglecting other substances: in this way, beriberi can be avoided.
Subject to the average daily dosages, B vitamins are not dangerous. Many of them, even when exceeding the norm, are easily excreted by the body. However, there are a number side effects, which can be observed when using vitamins of the group in question. These include:
- inflammation of the liver
- change in blood sugar levels,
- indigestion,
- change in blood pressure,
- disorder of the nervous system.
Normal side effects include discoloration of the urine.
Vitamin B1 during pregnancy
Thiamine, along with other vitamin and mineral compounds, is necessary for the full growth of the fetus and its intrauterine development. It is used for the normal course of all metabolic processes. Vitamin B1 is responsible not only for the energy supply of the baby's body, but also takes an active part in the formation of its nervous tissue. In addition, thiamine ensures the formation of a healthy heart, blood vessels and muscle fibers.
It is no less important for the pregnant woman herself, since it is involved in the functioning of the nervous system, it is necessary to maintain the mental and physical activity of the expectant mother. It also promotes rapid wound healing. Some experts claim that thiamine is the "vitamin of optimism" and improves mood. This, of course, is also important for bearing a healthy child.
Table. What destroys B vitamins and important points
| vitamins | Destructive factors | Important Points |
| Thiamine | Alcohol | Vitamin C protects thiamine from premature destruction |
| Riboflavin | Light | Riboflavin degradation products destroy vitamin C |
| Niacin | acids | The body synthesizes B3 from the amino acid tryptophan, which is found in protein-rich foods. |
| Pantothenic acid | heating, alcohol | Vitamin is poorly absorbed in case of problems with the intestinal microflora |
| Pyridoxine | Light, heating | Foods that have undergone heat treatment lose up to forty percent of this vitamin. |
| Biotin | Preservation, frying | To preserve this vitamin, do not soak foods for long time or fry them |
| Folic acid | Light, heating | Vitamin C and iron promote better folate absorption |
| cobalamin | - | With low acidity of the stomach, the vitamin is poorly absorbed. |
Characterization of thiamine
Today, many B vitamins have been discovered (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, B12, para-aminobenzoic acid, biotin, choline, inositol), which are actively involved in the course of vital functions: in metabolism, hematopoiesis, protein synthesis, fats, antibodies, hemoglobin, red blood cell formation, homocysteine metabolism, fetal development, regulation of nervous system activity. Their regular use can slow down the aging process and even reverse it.
The list of B vitamins is headed by thiamine, which is not able to accumulate in the body (see p. Causes of an increased need for thiamine).
As a result, in order to replenish the daily norm and prevent diseases associated with a deficiency of a substance, it is important to ensure its daily intake with food, supplements or medications.
Connection properties, how it is useful
- It is a colorless crystalline substance with a pronounced yeast odor, measured in milligrams.
- Dissolves in water. In fats, alcohol - no.
- Easily digestible. When ingested, more than 60% of thiamine is absorbed into the blood by diffusion in the small intestine. The rest is broken down by the enzyme thiaminase, which is found in raw fish meat, and is also produced by intestinal bacteria in the body. Up to 5 milligrams of vitamin B1 can be absorbed per day. In some cases, this figure reaches 15, but this is a rare exception to the rule and depends on the characteristics of the body. The state of the gastrointestinal tract has a direct effect on the degree of absorption of thiamine. The presence of diseases from the digestive system (ulcer, colitis, gastritis, pancreatitis) reduces the absorption of the vitamin by 3 or more times.
- The human or animal body daily produces an insufficient amount of vitamin B1 to meet the daily requirement for the substance. As a result, it must be regularly supplemented by introducing thiamine-rich foods or dietary supplements into the diet.
- Cocarboxylase (thiamine diphosphate) is a coenzyme of vitamin B1. The mechanism of its formation is as follows: initially, the thiamine molecule enters the bloodstream, then it goes to the largest digestive gland - the liver, where it combines with phosphoric acid residues and, with the assistance of magnesium, turns into thiamine diphosphate. As part of the coenzyme, the particle is transported to tissues, organs, where it participates in the course of biochemical processes.
- Resistant to acidic environment (with heat treatment up to 140 degrees). In alkaline or neutral solutions, thiamine is destroyed at 120 degrees or more. As a result, the addition of soda, ammonium carbonate to baking contributes to the rapid release and loss of vitamin B1.
- Muscles contain 60% of thiamine, 40% is found in the adrenal glands, brain, liver, heart, kidneys.
- Freezing foods rich in B1 by 50%, and sometimes completely, deprives them of a useful compound.
- When adding salt to peas, beans during cooking, the loss of thiamine is 75%. To maximize the preservation of the vitamin, the dish must be flavored after cooking.
- Lack of thiamine leads to beriberi, the development of the disease "take-take".
- Vitamin B1 becomes biologically inactive under the action of sunlight.
- Excess thiamine is non-toxic. When using vitamin B1 in large quantities (over 10 milligrams / day) after performing useful features the coenzyme molecule breaks down in the liver cells and, like the excess substance, is excreted in the urine.
Indications for admission
- diagnosed B-vitamin deficiency;
- neurological diseases;
- increased emotional stress;
- chronic fatigue;
- headache;
- sleep disorders;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- circulatory disorders;
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- diseases of the digestive organs;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- endocrine disorders;
- eye diseases (decreased visual acuity, cataracts);
- skin diseases (eczema, dermatitis, acne, seborrhea);
- damage to the skin and mucous membranes (wounds, ulcers);
- dryness and hair loss, brittle nails;
- osteochondrosis;
- radiation sickness;
- infectious processes;
- anemia;
- decreased immunity;
- recovery period after illness;
- active motor mode;
- intensive sports training;
- hard physical labor;
- harmful environmental conditions.
Effects on hair and skin
Thiamine has a direct effect on the condition of the hair, but the deficiency of the compound in the body does not immediately affect the structure of the curls. In 95% of cases, the first symptoms of nutrient deficiency are fatigue, irritability, nervousness, tachycardia, muscle weakness, and a decrease in blood pressure.
Then, due to violation metabolic processes, the hair loses its natural shine, elasticity and strength. To compensate for the lack of a nutrient, a daily intake of 1.5 milligrams of thiamine will help. If within six months the physiological need for the vitamin is fully met, the process of gradual fastening of the hair scales will “start”, and as a result, the problems that have arisen will be eliminated.

Appointment of thiamine for hair:
- strengthening curls;
- increased hair growth;
- slowing down the early appearance of gray hair;
- increase in color brightness;
- prevention of hair loss from the bulb;
- elimination of dry or oily seborrhea;
- saturation of the hairline with nutrients.
For accelerated restoration of the hair structure, in addition to oral administration, the drug can be additionally used externally, in the form of masks.
Ways to use vitamin in ampoules
- Rubbing undiluted product into the scalp. For this purpose, solution B1 of one ampoule is used, which is used to treat clean hair roots. After applying thiamine, you need to wait 30 minutes, then thoroughly rinse off the vitamin mask with warm water. This procedure is carried out once every 7 days for 2 months.
- Masks based on thiamine. Add 5 drops of liquid vitamin B1 to a portion of a cosmetic product (shampoo, conditioner, balm) and apply to the hair roots, evenly distributing the composition along the length. Wash off the mixture after 20 minutes.
Oral intake of the vitamin in combination with external hair treatment helps to eliminate the nutrient deficiency as soon as possible (in 3 months) and improve functional state skin and curls.
Before using thiamine, it is important to adhere to the following rules:
- Open the ampoule with a special file included in the package.
- When breaking off the tip of the ampoule, use a cotton pad.
- Do not use a solution opened a few hours ago. For the effectiveness of the procedures, the vitamin must be applied immediately after opening the vial, otherwise its effect is reduced by 50%.
- Detangle and carefully comb the hair before the mask.
- Apply thiamine with smooth movements to the hair roots. At the same time, it is important to avoid sudden intense actions that can damage weakened curls and lead to the bulb falling out.
- Before using the substance, make sure that its expiration date has not expired.
If pain occurs, the mask should be washed off immediately.
Given the fact that vitamin B1 maintains the elasticity of the skin, it is advisable to use applications based on it for facial skin.
Problems that thiamine effectively fights:
- wrinkles and sagging;
- peeling;
- excessive dryness of the skin;
- inflammatory processes, acne;
- vitamin deficiency of the skin;
- profuse pigmentation.
If the smell of a vitamin causes vomiting, it is likely that the person is allergic to that substance. To detect a negative reaction of the body, a drop of pure B1 should be applied to the elbow bend and kept for 15 minutes. In the absence of redness or burning in the “checked” place, the nutrient can be applied to the face. Applications based on thiamine help to normalize metabolic processes in the skin and regulate the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
How to use B1 for face
- Liquid vitamin is used in its pure form or in combination with other ingredients.
- It is important to use the nutrient within 10 minutes after opening the ampoule.
- The intensity of the use of undiluted "thiamine" applications - 2 times a week. The course of cosmetic procedures - 15 sessions. Cream enriched with vitamin B1 can be used daily.
- Before starting therapy, the skin of the face is thoroughly cleaned of cosmetics, then the composition is applied for 15 minutes, avoiding the area around the eyes and lips. After the specified time, the mask is washed off with warm water, the face is dried with a towel.
After the course procedures, in 90% of cases, the skin looks toned, fresh and elastic.
Recipe for anti-aging mask with thiamine:
- mix in equal proportions (15 milliliters each) warm linden honey, sour cream and cottage cheese (10 grams);
- add an ampoule of vitamin B1 to the prepared mixture;
- apply the composition to the cleansed skin of the face and neck;
- remove the remnants of the mask after 20 minutes;
- wash your face with warm water.
With regular use of this mask, wrinkles become less noticeable, the complexion evens out and acne decreases.
Contraindications
B vitamins should not be taken:
- with a tendency to allergic reactions;
- B1 - women before and during menopause, children under eight years of age;
- B2 - if any urolithiasis disease, simultaneously with the treatment of psychiatric disorders, while taking hormonal contraceptives;
- B3 - with gastric and duodenal ulcers in the acute phase, liver damage, gout, women during pregnancy and lactation, children under two years of age;
- B5 - with kidney disease in acute stage, hemophilia, intestinal obstruction, children under 3 years.
- B6 - with severe renal failure, gastric and duodenal ulcers during an exacerbation, coronary heart disease, functional liver disorders, thyroid diseases, children under 6 years of age;
- B12 - during pregnancy, lactation, if there are such diseases as: angina pectoris, erythremia, erythrocytosis and thromboembolism.
B vitamins should be taken with caution and under the supervision of a specialist if the following disorders are present:
- malignant formations;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- gout.
Pregnant and lactating women, the elderly, children should be prescribed vitamins by a doctor.
The historical aspect of the appearance
At the beginning of the 20th century, the biochemist Funk was able to obtain a nitrogen-containing compound from rice bran. The substance alleviated the symptoms of the beriberi disease, accompanied by damage to the emotional, mental and cardiac functions.
Only after a while, in the middle of the last century, the scientist Williams was able to describe the structure of the vitamin molecule (C12H17N4OS), which marked the beginning of the synthetic production of the substance. At the same time, the trivial name "thiamine" appeared, which replaced the obsolete at that time "aneurine". In addition, there are two more names for the substance - thiamine pyrophosphate and thio-vitamin.
Best B Vitamin Complexes
Many foods do not contain enough vitamins. All this is due to such factors as: poor soils, dyes, preservatives, new technologies for processing and processing products. Therefore, specialists have developed preparations containing vitamins of group B. Of the highly effective complexes sold in pharmacies, the following can be distinguished:
RATIOPHARM VITAMIN B COMPLEX

The average price is 2707 rubles. Manufacturer - Germany. The most effective of the premium drugs. Ratiopharm is a company that has won the trust of those who are used to taking care of their health. The complex includes all active compounds of the B-group. Ratiopharm Vitamin B Complex:
- supports the nervous system;
- controls protein metabolism;
- increases efficiency;
- strengthens the immune system.
With regular use of the drug:
- mood improves;
- increased concentration of attention;
- the level of hemoglobin increases;
- cells of the skin and mucous membranes are restored.
The disadvantages of this tool are the high cost and the possibility of side effects.
The complex can cause:
- heartburn;
- backlash (decrease in efficiency).
In most cases, the drug has a positive effect on the body: it improves well-being and improves immunity. The action of the multivitamin is approved by numerous reviews.
Kombilipen
Price - 470 rubles. Manufacturer - Russia. The complex contains vitamins B1, B6, B12. It is an analogue of the drug "Milgamma", intended for the treatment of neurological diseases.
The drug "Combilipen":
- has an analgesic effect;
- promotes the restoration of nerve tissues and myelin fibers.
Vitamin B1, which is part of the composition, has a fat-soluble form - benfotiamine, due to which its bioavailability increases several times. The complex contains high dosages of B1 and B6 (100 mg each) and a small dose of B12 (2 mg).
Contraindications to taking the drug:
- cardiovascular insufficiency (acute and severe forms);
- childhood.
Blagomax
The average price is 190 rubles. Manufacturer - Russia. The product is available in capsules. The package contains 90 pcs. The number of capsules is calculated for 3 months of admission (according to the instructions, the daily dose corresponds to 1 capsule). Blagomax is one of the the best complexes B-groups at an affordable price. Ingredients: vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, B8, B9, B12.
Main functions:
- stabilization of the nervous system;
- acceleration of metabolism;
- vasodilating action;
- improvement of blood circulation;
- normalization of hematopoietic processes;
- lowering cholesterol levels;
- improving the functioning of the digestive organs;
- maintenance of visual processes.
Indications for admission:
- increased physical and mental stress;
- stressful conditions.
The effectiveness of the drug is confirmed by many positive reviews. The authors note that as a result of taking vitamins:
- improves well-being;
- irritability decreases;
- the quality of sleep improves;
- metabolism is normalized;
- improves the condition of the skin, hair, nails.
The use of the drug is contraindicated in women during pregnancy and lactation.
Pentovit
Price - 112 rubles. Manufacturer - Russia.
The composition of the drug includes vitamins: B1, B3, B6, B9, B12.
Indications for use:
- asthenic conditions;
- neuralgia;
- recovery period after illness.
The lack of a vitamin complex is a relatively large number of contraindications.
The drug should not be taken:
- with chronic form of pancreatitis;
- people suffering from gallstone disease;
- women during pregnancy and lactation (nicotinamide, which is part of the composition, is toxic to the embryo and baby);
- children under 18 years of age.
"Mega B Complex"
The complex contains all B group vitamins. "Mega-B Complex" supports the functioning of the nervous system, so it is especially needed for those who are constantly nervous or engaged in heavy physical labor. Due to the presence of calcium in the composition, the exchange of vitamins between the cell walls improves. This improves the overall positive effect on the body.
Vitamins protect cells and mucous membranes from aging, restore the integrity of the skin.
The entire daily norm of vitamins is contained in one tablet. Adults should take one tablet daily for 1-2 months.

The preparation contains the whole complex of vitamins of group B, is prescribed for severe hyperavitaminosis of vitamins B1 and B6 (neuralgic diseases of the musculoskeletal system). Increases blood flow, activates the nervous system.
The composition includes additional components:
- Pyridoxine hydrochloride, which affects the process of protein metabolism;
- Benfotiamine, a derivative of vitamin B1 involved in the oxidation of glucose;
- carmellose sodium;
- Incomplete glycerides of higher fatty acids;
- Talc.
Pyridoxine is involved in the production of serotonin, the hormone of pleasure, which alleviates unpleasant symptoms in diseases.
Indications for use:
- neuritis (paralysis or paresis);
- retrobulbar neuritis (loss of vision);
- neuralgia (peripheral nerve damage);
- ganglionitis (inflammation of the ganglion - nerve node);
- paresis of the facial nerve (impaired functioning of facial muscles);
- lumbar ischialgia (back pain);
- polyneuropathy, neuropathy;
- plexopathy (damage to the nerve plexuses);
- radiculopathy (sciatica).
The drug is taken 1-3 times a day for one month. One package containing 60 tablets (enough for a month or two) costs 1000 rubles.
"Angiovit"
Vitamin complex contains:
- vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) - 0.006 milligrams;
- vitamin B6 (pyridoxine hydrochloride) - 4 milligrams;
- folic acid - 5 milligrams.
A specially designed complex is taken for: insufficient blood circulation of the brain, angiopathy (damage to blood vessels), diabetes, atherosclerosis.
The drug improves the metabolism of proteins, in particular methionine (an essential amino acid), as well as its catalysts (process accelerators). Therefore, the complex prevents diseases such as:
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- arterial thrombosis;
- ischemic cerebral stroke;
- heart attack (myocardium);
- diabetic vascular disease);
- chronic miscarriage of the fetus;
- congenital pathology in a child.
Angiovit is useful in the treatment of elderly dementia, depression, Alzheimer's disease.
Vitamins are rapidly absorbed in the intestine after ingestion. Contraindications are only individual intolerance to the components. Side effects rarely occur in the form of allergies: swelling, urticaria, itching of the skin. Tablets should not be chewed or crushed, they must be swallowed and washed down with water.
The duration of the treatment course is 20-30 days. Take one tablet per day, preferably in the morning. So the body will be saturated with a complex of vitamins of group B for the whole day.
"Neuromultivit"
This complex includes:
- vitamin B1 - 0.1 grams;
- vitamin B6 - 0.2 grams;
- vitamin B12 - 0.2 grams.
- and other excipients: microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, povidone + components included in the tablet shell.
In addition to group "B", it also contains vitamins: A, D3, C, as well as minerals: calcium, phosphorus, which help their absorption.
You can not take the drug:
- Pregnant, lactating mothers;
- Children under 12;
- Patients with diabetes;
- Hypersensitive to the components of the complex;
The active components of the drug - B1, B6 and B12 - are used in the treatment of not only beriberi, but also diseases that do not depend on metabolism: pain syndrome, polyneuritis, psychosis.
Indications for the use of the drug are:
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- polyneuritis (diabetic and alcoholic polyneuropathy);
- neuritis (inflammation of peripheral nerves);
- damage to the sciatic nerve caused by its inflammation or compression (sharp back pain) and lumboischialgia;
- radicular syndrome (sciatica);
- neuropathy of the facial nerve.
Possible side effects: nausea, tachycardia and skin rashes.
Neuromultivit should be taken "whole", without crushing the tablet, immediately after a meal. Number of doses per day: from one to three. You need to take the drug for no more than one month.
Gerimaks
Ingredients: all the necessary vitamins of group B, as well as vitamins of other groups, minerals, extracts: ginseng, green tea.
It is excellent for insomnia, heavy physical and mental stress. After a working day, energy remains, a person feels invigorated due to ginseng extract. The drug helps with beriberi, increases energy metabolism.
Who should not take:
- Teenagers under 16;
- Patients with excess calcium in the body;
- With increased sensitivity and excitability;
- Patients with hypertension.
Who needs to take:
- People experiencing stress when playing sports or strenuous studies;
- Patients during the rehabilitation period;
- Insomniacs;
- With a lack of vitamins and minerals.
In case of an overdose, itching of the skin, digestive and sleep disturbances are possible. It is best to take Gerimaks after breakfast.
Taking drugs with B vitamins will certainly help to establish metabolism and cure diseases. You just need to make sure and consult with your doctor, because the complexes, as you have seen, are different and at the moment there are many of them.
Afterword
To stay healthy, most people can get everything they need if they eat a varied, balanced diet with vitamin B rich foods such as leafy greens, nuts, legumes and grains, dietary protein, mushrooms, and eggs. If you are not deficient in vitamin B, there is no need to take extra, but sometimes there are indications for use.
If you are not getting enough synthesized vitamin B from food, then it may be helpful to turn to nutritional supplements, whose effect on the body is beneficial. Its deficiency can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, anemia, loss of appetite, depression, abdominal pain, muscle cramps, hair loss and eczema.
Most importantly, do not forget to consult with your doctor and find out which vitamin complex is right for you (and if you still need it, how much of it you need, taking into account what you get from food and other sources).
Disclaimer: The information contained on this site is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for advice, diagnosis, or treatment by a licensed physician. It is not intended to cover all possible precautions, drug interactions, circumstances or side effects. You should apply for medical care for any health concerns and consult your physician before using alternative medicine or making changes to your regimen.
Conclusion
Vitamins "B" are indispensable for the body. It is important to prevent the appearance of a deficiency of nutrients.
And also we must not forget about the overabundance of these vitamins, which can harm the body.
When choosing one or another vitamin complex of this group, consult your doctor.
Rate the material:
Ratings: 6
(4,83
out of 5)
Admin
Found an error? Select it and click Ctrl+Enter
Report a bug
Vitamin B4 (choline): description, characteristics. Benefit and harm to the body
Vitamin P (Rutin, Bioflavonoids): description, in which products, benefits and harms

The history of the discovery of vitamin B1
The detection of vitamin B1 is associated with the pathology "beri-beri", which in fact is a pronounced deficiency of B1 and means "hurts - hurts." Now such diseases, fortunately, practically do not occur. It was common at the beginning of the 20th century among the inhabitants of Asian countries, who ate mainly white rice. Rice stripped of its shell did not provide the daily intake of vitamin B1, as a result of which people suffered from various disorders of the brain and peripheral nerves (the so-called "dry vitamin deficiency B1"), as well as the cardiovascular system (or "wet vitamin B1 deficiency", which accompanied by severe edema).

Typical appearance of a beriberi patient
Patients with "beri-beri" experienced poor appetite and nausea, frequent constipation, constant pain and tingling in the limbs, sleep disturbances up to insomnia, frequent mood swings, a significant decrease in mental and physical activity. Soreness in the calf muscles when walking did not allow even daily activities. In the extreme stage, paralysis of internal organs and muscles developed. Damage to the heart and blood vessels led to edema, lowering blood pressure and the development of heart failure.
A close study of this pathology by a Dutch doctor and Nobel laureate Christian Aikman(Christiaan Eijkman) led him to assume that the grains of rice contained some kind of paralytic substance. At the same time, rice bran contains useful material that prevent the development of the disease.
As early as 1911, the Polish-American biochemist Kazimierz Funk received a bioactive substance from rice bran, later called simply “vitamin” (from the Latin vita + amin).
In 1926 the Dutch biochemist Barend Coenraad Petrus Jansen And William Frederick Donat isolated from rice bran pure vitamin B1 in crystalline form. Historically, it was the very first pure vitamin. Hence the name "B1", i.e. vitamin number 1.
It is noteworthy that one of the names of vitamin B1 is aneurin. It refers to a substance that prevents damage to the nervous tissue. Later, due to its chemical (amine) structure, vitamin B1 became known as thiamine(lat. Thiamine). This name stuck with him and is widely used to this day.
Benefits and Benefits for Human Health
#1 Treatment for Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is one of the most severe neuropsychiatric consequences of alcohol abuse. The authors of the 2013 Cochrane review of thiamine for the treatment or prevention of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome found only two studies that met their inclusion criteria, and one of these studies was not published.
These randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials compared 5 mg/day orally for 2 weeks or daily intramuscular doses of thiamine from 5 to 200 mg/day for 2 consecutive days in 177 people with a history of chronic alcohol use. The authors of the Cochrane review concluded that there is insufficient evidence from randomized clinical trials to provide guidance to healthcare professionals on the appropriate dose, frequency, duration, or route of administration of thiamine for the treatment or prevention of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome in patients who abuse alcohol.
The authors of the European Federation of Neurological Societies guidelines for the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of Wernicke's encephalopathy note that even high doses of oral thiamine supplements may not be effective in increasing blood levels of thiamine or treating Wernicke's encephalopathy. They recommend 200mg of thiamine, preferably intravenously, three times a day (600mg/day total) until signs and symptoms subside, along with a balanced diet.
In their guidelines for the management of Wernicke's encephalopathy in emergency departments, the Royal College of Physicians London supports the administration of oral thiamine hydrochloride (100 mg three times daily) to patients with adequate dietary thiamine intake and no signs or symptoms of Wernicke's encephalopathy. However, the authors recommend parenteral thiamine supplementation for high-risk patients, such as those with ataxia, confusion, and chronic alcohol abuse, because oral supplementation is unlikely to provide adequate blood levels.
#2 Preventing Beri Beri Disease
The most common effect of thiamine deficiency is vitamin deficiency (Beri-Beri disease), which is characterized mainly by peripheral neuropathy and malnutrition. People with this disease have impaired sensory, motor, and reflex functions.
Beri-Beri is most commonly seen in people who abuse alcohol, but may also be associated with other etiologies leading to thiamine deficiency.
Initially, symptoms of beriberi are nonspecific and include constipation, appetite suppression, nausea, mental depression, fatigue, peripheral neuropathy, anorexia, and weight loss. With progression chronic symptoms may begin to appear as wet beriberi or dry beriberi. Wet beriberi have edema, an enlarged heart, heart failure, warm extremities, pleural effusions, and pulmonary edema. Meanwhile, the complications of dry avitaminosis are predominantly neurological with damage to the peripheral nervous system. People with dry beriberi may have paresthesia, foot drop, muscle atrophy, numbness, and lack of ankle reflexes.
In rare cases, beriberi causes congestive heart failure, which leads to swelling in the lower limbs and, sometimes, to death. Although beriberi is rare in developed countries, people in these countries sometimes get sick [ , ]. The introduction of additional thiamine, often parenterally, quickly cures beriberi.
#3 Diabetes mellitus
Some small studies have shown that oral thiamine supplements 150–300 mg/day can lower glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance [ , ]. However, the authors of these studies did not assess the potential clinical relevance of these findings.
Several small randomized trials have evaluated the effects of benfotiamine supplementation on diabetic neuropathy. Three studies found that, compared with placebo, benfotiamine 120–900 mg/day with or without other B vitamins reduced neuropathic symptoms and decreased urinary albumin excretion (a marker of early-stage diabetic nephropathy) [ , ]. However, another study found no effect of 900 mg/day benfotiamine on urinary excretion of albumin.
Well-designed studies with larger sample sizes and longer durations are needed to determine whether thiamine supplementation can lower glucose levels in patients with diabetes or reduce diabetic complications.
#4 Heart failure
Rates of poor thiamine status in heart failure patients ranged from 21% to 98% across studies. Explanations for this association include advanced age, comorbidities, insufficient food intake, diuretic treatment, and frequent hospitalizations.
The authors of one study reported that 33% of 100 patients with chronic heart failure were deficient in thiamine compared to 12% of 50 healthy volunteers. The deficiency rate was even higher when the researchers excluded those who took thiamine supplements. The varying incidence of thiamine deficiency in patients with heart failure in these and other studies is likely due to differences in nutritional status, comorbidities, medications and dietary supplements used, and methods of measuring thiamine status.
The authors of a systematic literature review and meta-analysis found two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of thiamine supplementation in people with heart failure that met their eligibility criteria. In these studies, thiamine supplementation significantly improved the net change in left ventricular ejection fraction. However, the authors did not assess the clinical significance of this finding.
More research is needed to determine if thiamine supplements can help people with heart failure, even if they have a normal thiamine status.
#5 Alzheimer's disease
According to animal model studies, thiamine deficiency may play a role in the development of Alzheimer's disease. For example, thiamine deficiency causes oxidative stress in neurons, neuronal death, memory loss, plaque formation, and changes in glucose metabolism are all markers of Alzheimer's disease. Autopsy studies have shown that transketolase and other thiamine-dependent enzymes reduce brain activity in people with Alzheimer's disease [ , ].
Few studies have assessed the prevalence of thiamine deficiency in people with Alzheimer's disease. One of these studies found that 13% of 150 patients with cognitive impairment and acute behavioral disorders were considered thiamine deficient based on plasma levels.
The authors of a 2001 Cochrane review evaluated three double-blind, randomized trials (including two cross-over trials) comparing the effects of oral thiamine 3 g/day with placebo on cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer's dementia. Three studies randomly assigned fewer than 20 patients. The review authors stated that it was not possible to draw any conclusions from these three studies because they were small and the publications that described them did not provide enough detail to combine these data in a meta-analysis.
Larger, well-designed studies are needed to determine whether thiamine supplements are beneficial for treating Alzheimer's disease.
#6 Cataract
Recent studies show that thiamine may reduce the risk of developing cataracts. These studies show that people who consume a lot of protein along with vitamins A, B1, B2 (riboflavin) and B3 (niacin) in their diet are less likely to develop cataracts. Getting enough vitamins C, E and B vitamins additionally protects the lens of the eye ().
#7 Benfotiamine, a Thiamine Analogue, Can Suppress Cancer Growth
Benfotiamine has been shown to inhibit the growth of leukemic tumors in cell studies by promoting cell death and enhancing the effects of chemotherapy.
Benefit for health
The processes listed above affect the general condition of the body, the work of internal organs and systems. As a result, the properties of the outer covers are improved, since tissue nutrition is normalized.
B group vitamins promote hair growth, help maintain them in good condition: affect pigment, work sebaceous glands.
This means that preparations based on these components provide a complex effect on the body. They not only improve the appearance of curls, but also eliminate the causes of the pathological condition.
Functions of thiamine in the body
Thiamine affects almost all body systems, providing a therapeutic and prophylactic effect. This is due to its functions in the body.
metabolic
- ensuring the correct course of metabolic processes;
- production of energy molecules ATP;
- absorption of proteins and fats from food;
- production of blood cells.
nervous
- the formation of myelin sheaths around nerve endings;
- mood enhancement;
- memory improvement;
- depression treatment;
- reducing the impact of stress;
- treatment of cerebellar syndrome.
Cardiovascular
- ensuring the normal functioning of the ventricles of the heart;
- treatment of arrhythmias;
- prevention of heart failure.
digestive
- maintaining the muscle tone of the digestive tract;
- normalization of the secretion of hydrochloric acid.
visual
- prevention of glaucoma and cataracts;
- strengthening the eye muscles;
- protection of the optic nerve.
Mistakes that lead to a decrease in vitamin B1 levels
You should not assume that eating a handful of sunflower seeds or a couple of pine nut kernels, you can not worry about the level of thiamine in the blood: the need for this substance, as well as its absorption, can vary significantly depending on the physiological characteristics of the body, addictions and lifestyle itself. person. The most common mistakes are as follows:
- Thiamine is rapidly destroyed by heat treatment. This once again proves that fresh products are much healthier and more nutritious than cooked ones.
- In an acidic environment, vitamin B1 is more resistant to high temperatures than in an alkaline and neutral one. That is why baking soda contains a lower percentage of thiamine than a similar dessert without sodium bicarbonate.
- Freezing useful products in the freezer leads to the partial destruction of thiamine molecules. Depending on the specific type of food product, the damage caused can vary between 50-90% of the original level of the vitamin.
- Canned foods are depleted in vitamin B1 even if critically high temperatures were not reached during their preparation. In just half an hour of sterilization, without which safe preservation is impossible, up to 40% of thiamine is destroyed.
- Coffee drinkers should double or even triple their daily intake of vitamin B1, as the invigorating drink stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid, which in large doses inhibits the action of thiamine.
Eat healthy foods, rationally approach menu planning, follow the correct lifestyle without waiting dangerous symptoms, - only in this way you can maintain your own health and good spirits for many years of life!
Usage
The role of vitamin B1 in the body is great, so it is often prescribed. It is useful for:
- B1 deficiency;
- chronic diseases of the digestive organs, accompanied by low acidity and impaired absorption of food in the intestine;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- polyneuritis;
- exhaustion;
- muscle weakness;
- heart disease with heart failure;
- angina pectoris, myocardial infarction;
- myocardial dystrophy - the so-called metabolic diseases of the heart muscle;
- skin diseases accompanied by itching (eczema, psoriasis, shingles, etc.);
- chronic alcoholism;
- lactation disorders - stimulates the production of women's milk;
- poisoning;
- as part of complex therapy to eliminate pain;
- infants who eat only semolina.
Vitamin B 1 is produced in the form of drugs and biologically active food supplements (BAA). These funds are called differently. How to take drugs with vitamin B1, the doctor determines.
- Benfogamma - 1 tablet contains 150 mg of a fat-soluble vitamin with high bioavailability; the tablet should be taken 1 time per day, after meals; the drug is especially useful in neurological diseases;
- Thiamine chloride and thiamine bromide - the dosage of a water-soluble compound in tablets can range from 2 to 100 mg; take half an hour before meals; for prophylactic purposes, adults are prescribed 5 mg daily, children from 3 to 8 years old - 2 mg each, up to 3 years old - 1 mg each.
- Phosphotiamine - the active substance is monofostiamine - phosphoric ester of thiamine; prescribe 10 mg after meals for a course of 3 to 4 weeks.
Solutions in ampoules with vitamin B1 (thiamine) are prescribed only by a doctor strictly according to indications. Most effective drug is cocarboxylase - active thiamine, necessary to increase the energy potential of cells, is produced in the form of a powder in ampoules for the preparation of an injection solution.
Recipe for tablets:
Rp.: Thiamin chloridi 0.002
D.t.d. No. 50 in tab.
S. Take 1 tablet 3 times daily
Scalp massage with vitamins
You can apply the above means in another way - by rubbing into the scalp. In this case, the active components fall directly to the lesion. You will need cyanocobalamin, thiamine or pyridoxine hydrochloride.
If the symptoms of the disease are mild or moderate, it is enough to choose one substance - 4 ampoules. It is permissible to combine them: take 2 types of vitamins (2 ampoules of each).
The solution must be prepared in a plastic or porcelain dish. If you do not follow this recommendation, useful substances will quickly collapse.
The head must first be washed. The composition is applied with a syringe, it is rubbed with fingertips. For convenience, it is recommended to separate the curls with partings. After processing, it is not necessary to wash off the product.
Useful substances that are used for massage do not stain the scalp. After the procedure, it is permissible to dry the hair with a hairdryer. The frequency of performing massage - 3 times a week. Course duration - 1 month.

Head massage with B vitamins.
Foods Rich in Vitamin B1
- wholemeal wheat bread
- cereals (coarse rice, oatmeal, buckwheat, millet)
- legumes (soybeans, beans, green peas, lentils)
- greens (spinach, parsley, onion)
- vegetables (asparagus, broccoli, spinach, potatoes, carrots, white cabbage, Brussels sprouts, pumpkin, cauliflower, tomatoes, beets, eggplant)
- offal (liver, kidneys, lungs, heart, stomach, brain)
- meat (pork, beef)
- egg yolk
- yeast (beer)
- algae (kelp, spirulina)
- milk
- nuts (pine nuts, pistachios, peanuts) and sunflower seeds
- fruits and berries (oranges, rose hips, plums, strawberries, blueberries, black currants, sea buckthorn)
- dried fruits (prunes, raisins)
- herbs (alfalfa, peppermint, raspberry leaf, sage, clover, sorrel, burdock root, catnip, cayenne pepper, fennel seeds, chamomile, fenugreek, hops, nettle, oat straw).

Physico-chemical features
Vitamin B1 is a crystalline powder with high biological activity. It is soluble in water but insoluble in alcohol. There is also a fat-soluble synthetic derivative of thiamine - benfotiamine. When heated, vitamin B1 decomposes and loses its healing properties. There are four forms of this substance in the human body:
- unphosphorylated thiamine,
- thiamine monophosphate,
- thiamine diphosphate (thiamine pyrophosphate - TPP, TDP, cocarboxylase) - the most common active form,
- thiamine triphosphate (TTP) is an understudied form.

The chemical formula is C12H17N4OS.
The biological properties of vitamin B1 are due to the action of TPP (TDF), which is formed from thiamine and ATP in the presence of the enzyme thiamine kinase. This active form of vitamin B1 is a coenzyme (component) of enzymes that play an important role in metabolic processes. Enzymatic reactions involving TPP (cocarboxylase):
- It is a transketolase coenzyme involved in the renewal of liver cells, erythrocytes, adrenal cortex, etc. These enzymatic reactions of glucose oxidation are not associated with the formation of energy, they provide protein synthesis processes.
- As a coenzyme for the enzymes pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, it is involved in energy metabolism. The received additional energy goes to the activation of all metabolic processes.
- As a coenzyme dehydrogenase contributes to the breakdown of a number of amino acids.
It is believed that such a little-studied form as TTP is involved in the formation of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and the transmission of impulses through the nervous system.
Composition and characteristics of B vitamins
This group includes:

Characteristics and properties of B vitamins.
- Vitamin B1. It is a water-soluble substance, its other name is thiamine. Main characteristic is intolerance to high temperature (the vitamin begins to break down). With its participation, metabolic processes develop: proteins, fats, carbohydrates are transformed in the body, thanks to which the substance contributes to the normalization of the nutrition of the scalp, hair follicles. It is contained in soft tissues, but does not accumulate, because it dissolves in water. Other functions: stimulation of cell growth, restoration of the nervous system, which also helps to improve the condition of the hair.
- Riboflavin, or vitamin B2. It is a water-soluble substance, which means that it is quickly destroyed in the body. Participates in most metabolic processes, since it is a coenzyme. The main function is to maintain redox reactions. Thanks to them, harmful substances are destroyed, and useful compounds, on the contrary, are protected from the negative effects of free radicals. This improves the condition of soft tissues (scalp) and hair. Riboflavin affects the functioning of the sebaceous glands, activates regeneration.
- Vitamin B3, also called niacin or nicotinic acid. This substance also affects metabolic processes, participates in the transformation of lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, restores tissue respiration, and lowers the concentration of low density lipoproteins. Vitamin improves blood circulation due to the ability to dilate blood vessels. These processes allow you to activate the nutrition of the scalp and hair. The substance affects pigmentation, and also gives shine and strength.
- Vitamin B4. Another name is choline. It releases the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. With his participation, the process of transmission of nerve impulses is realized. Vitamin affects carbohydrate metabolism, performs the function of a hepatoprotector, is involved in the transport of fats. This means that it acts on the scalp and hair indirectly, normalizing internal processes in the body.
- Pantothenic acid, or vitamin B5. The substance affects metabolic processes. Its main function is the transport of carboxylic acids. Thanks to this vitamin, hair loss stops, their condition normalizes, since it affects the production of hormones.
- Vitamin B6 (adermine). Most often, one of the derivatives, pyridoxine hydrochloride, is used to restore body functions. In its pure form, the component is not used. The substance is involved in metabolism, affects the synthesis of neurotransmitters, histamine, hemoglobin. As a result, the condition of tissues and hair is normalized, since the work of the nervous system improves, tissue respiration is restored.
- Biotin, or vitamin B7. The substance is involved in the metabolism of fatty acids, carbohydrates, proteins, the process of gluconeogenesis, promotes the synthesis of collagen, thereby improving the condition of tissues and hair.
- Vitamin B8 (inositol). It is part of enzymes, affects lipid metabolism, normalizes cholesterol levels. This means that it is used to improve the condition of the hair as an indirect measure of influence, for this, internal processes are first restored.
- Vitamin B9, or folic acid. The substance has a positive effect on the immune and circulatory system, thereby improving the nutrition of tissues and follicles. Vitamin affects the synthesis of cells, their growth.
- Vitamin B10. This substance helps to increase the effectiveness of other B vitamins. It is distinguished by antioxidant properties that slow down the aging process. Vitamin helps to remove gray hair, smoothes wrinkles, cleanses the skin.
- Vitamin B11, or L-carnitine. Involved in metabolic processes. Due to this, tissue repair and regeneration is accelerated.
- Vitamin B12. It is called cyanocobalamin. The substance is involved in enzymatic reactions, avoids the development of anemia, thereby improving the nutrition of tissues, their respiratory function. Deficiency of cyanocobalamin (B12) can lead to nerve cell death.
Release form
When choosing how to take a B vitamin, you must first determine the form and dosage. The drug is available in two forms: solution for injection and tablets or capsules for oral administration. Each of these forms has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The advantages of the solution for injections are high bioavailability and fast appearance of the result. Injection is not suitable for young children, because they do not always agree with injections, as well as for older people - it is more difficult for their body to cope with a possible overdose. This method of administration is more often used in acute hypovitaminosis and is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor.
Oral tablets or capsules are easy to use and help you control how much you take. But such agents have lower bioavailability due to the fact that some of the active substances are destroyed in the gastrointestinal tract. Oral forms can be drunk at home and are safer than injections.
Probably, there is not a single person who has not heard the word "vitamins" and has no idea about their benefits. We will try to answer the following questions:
Vitamins - what is it?
Why are they needed?
What diseases occur due to beriberi?
What foods are included?
What interferes with the absorption of vitamins?
What helps?
The word "vitamins" was introduced into circulation at the beginning of the twentieth century by K. Funk. Translation from Latin is short and clear - life. Vitamins are a fairly large group of substances that are completely different in chemical structure. And they are united in one group, as they are vital for the body. They are found in food.
It was believed that only the energy component of food (calories) was needed to nourish the body. But it was noticed that in the absence of certain foods in the diet (even with sufficient calories), a person begins to get sick. The study of the composition of food began more carefully. It was found that some substances that enter the body with food are involved and whether they are catalysts for processes occurring in the body. Vitamins, with rare exceptions, are not synthesized directly in the body, they must be obtained from food. Some are accumulated and stored in the organs of the body (fat soluble), then there is no need to consume them daily, others must be taken daily (water soluble).
Pathologies arising from an imbalance associated with the intake of vitamins in the body:
Avitaminosis - absence;
Hypovitaminosis is a deficiency;
Hypervitaminosis is an excess.
Now the synthesis of all vitamins is possible, so their deficiency can be replenished with vitamin complexes. They can be used as dietary supplements as directed by a physician. But a well-balanced healthy diet allows you to get all the vitamins from food.
A person needs a balanced healthy diet, since he can get vitamins only from food.
VITAMINA (retinol)
Fat-soluble, converted from beta-carotene.
Carotene is found in yellow and orange vegetables (carrots, pumpkin), greens (parsley), is found in the liver of fish, fish oil, egg yolk.
Benefit:
It is very useful for vision, with a deficiency, "night blindness" is observed (a person does not see anything at dusk);
It has a good effect on the mucous membranes of the body, helps in their restoration (intestines, genitals, oral cavity);
Useful for strengthening bone tissues (bones, teeth, gums) and bone growth, strengthens hair follicles, promotes hair shine;
Increases the body's resistance;
Accelerates the reaction, increases efficiency.
Enemies of vitamin A: oxidized in air, destroyed by ultraviolet light, zinc deficiency in the body leads to a slowdown in the absorption of vitamin A.
Friends: vitamin E protects against oxidation, and zinc contributes to better absorption.
VITAMINSGROUPS B
There are a lot of vitamins of this group, they are combined general principle: in the presence of B vitamins, the activity of a whole group of enzymes is manifested, which affect the chemical reactions of the body. In the absence of the vitamin, no chemical reaction occurs.
VITAMINB 1 (thiamine)
A water-soluble vitamin, due to the presence of sulfur in the chemical compound. Thiamine has a characteristic odor.
Found in yeast, nuts, legumes, sprouted wheat, cereals, added (artificially) to flour.
Benefit:
carbohydrate metabolism;
Promotes the complete combustion of carbohydrates in cells;
With a deficiency, toxins accumulate in the body;
Use in high doses has no side effects;
Improves the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
Normalizes the acidity of the stomach;
Affects intestinal motility;
Increases the body's defenses;
Improves brain function.
Enemies: sugar, alcohol, smoking, caffeine - destroy thiamine, is easily washed out, when cooking it is better not to boil, but to steam.
Friends: magnesium helps to transfer thiamine to the state in which it takes part in the work of the body, does not break down into its constituent parts at high temperatures (up to 150 degrees), fish oil, vegetable fat save thiamine.
VITAMINB 2 (riboflavin)
Not produced in the body, which is a yellow pigment.
Contained in cabbage, yellow vegetables, dairy and animal by-products, yeast.
Benefit:
The main action is protection from excessive ultraviolet radiation;
Improves vision, provides color perception;
It is a catalyst for redox reactions;
Helps in the metabolism of basic substances;
Promotes the formation of red blood cells;
Affects the renewal of all body tissues, is necessary for children and the fetus, helps in the growth of the body;
Participates in the synthesis of hormones;
Increases hemoglobin.
Enemies: some medicines(antidepressants), ultraviolet.
Air, heat, acidic substances do not destroy the vitamin.
VITAMINB 3 (pantothenic acid, panthenol)
In nature, it is found almost everywhere, therefore it is called "ubiquitous", it is an organic acid containing nitrogen.
Found in green leafy vegetables, all kinds of nuts, liver.
Benefit:
Participates in the breakdown and exchange of the main energy-containing components of food;
Helps to produce red blood cells, cholesterol;
Helps in the work of the brain;
Improves psychological condition;
Helps maintain muscle tone;
Treats skin diseases, heals wounds on the skin;
Stimulates the work of the intestines, adrenal glands;
Used as nutritional supplements in muscle building exercises;
Affects the body's resistance;
Reduces the harmful effects of alcohol.
Enemies: No heat manipulation allowed.
Friends: interacts positively with water-containing vitamins.
VITAMINB 6 (pyridoxine)
With food come vitamins that take part in the work of the body without chemical reactions with them.
Contained in poultry, eggs, wheat, lean meats, bell peppers, various types of cabbage.
Benefit:
Provides metabolism, especially protein;
Takes part in the production of many enzymes;
Slows down the aging of the body;
Supports the immune system, synthesizes antibodies;
Reduces the risk of cramps and numbness;
Affects the production of hemoglobin;
Strengthens the nervous system;
Reduces the risk of atherosclerosis.
Friends: the mutual influence of magnesium and cobalamin is favorable.
Enemies: smoking, long-term storage is not recommended, withstands heat treatment for a very short time, is destroyed in the presence of female sex hormones, is not compatible with alcohol.
VITAMINB 12 (cyanocobalamin)
An organic compound, rather complex in structure, the only vitamin containing cobalt. Synthesized by fungi and bacteria. Formed in the body and stored in the liver.
Contained in seafood, a little in poultry, accumulates in the liver, so the content in the liver of all living organisms and fish is high.
Benefit:
- Participates in hematopoiesis;
- Without the participation of this vitamin, DNA synthesis is impossible;
- Provides cell division;
- Affects fat and protein metabolism;
- Used to improve appetite;
- Helps with a lack of hemoglobin;
- Supports the organism weakened as a result of irradiation;
- Helps in the treatment of nervous diseases;
- Improves memory.
Enemies: Turns inactive when illuminated.
Friends: the need for interaction with calcium, is not destroyed by high temperatures ah, long-term preservation in the dark is possible.
VITAMINB C (folic acid)
The combination of certain acids with a yellow pigment (glutamic acid).
Found in leafy greens, legumes, carrots, onions, mushrooms, eggs. Needs additional processing in the body.
Benefit:
Participation in the synthesis of blood cells;
Catalyst of biochemical processes;
Increases hemoglobin;
Helps normalize protein metabolism;
Promotes cell renewal.
Enemies: destroyed during cooking, food processing, in the light, with an increased hormonal background of the female type.
Friends: B vitamins. B-vitamin cocktails will help with migraines.
Side effects and overdose: allergic reactions. Like all water-soluble vitamins, it is excreted from the body in case of overdose, no toxicity is noted, in rare cases, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, increased excitability, and unusual dreams are possible.
VITAMINC (ascorbic acid)
Non-synthesized in the body substance of plant origin only
Found in all foods of plant origin.
Benefit:
Increases immunity;
Takes part in cleansing the human body of toxins and processed products;
Strengthens blood vessels;
Does not allow some fats to oxidize;
Promotes healing of wounds and burns;
Useful for any disease.
Enemies: oxygen, oxidized presence, heat and light processing, storage, smoking, not compatible with B 12, consumption in large quantities can lead to the formation of kidney stones.
Friends: well preserved in any acidic environment
VITAMIND (calciferol)
A family of fat-soluble compounds formed from sterol under the action of ultraviolet light.
Contained in fish oil and fatty fish, formed in the skin under the influence of UV - rays.
Benefit:
- The main purpose is to preserve the structure of bone tissue;
- Helps to remove heavy metals from the body;
- Contributes to the normalization of blood clotting;
- Helps in preventing colds;
- Destroys certain types of microbes;
- Essential for baby food.
Enemies: Hardly compatible with iron, polluted atmosphere interferes with vitamin production.
Friends: helps the absorption of magnesium.
VITAMINE (tocopherol)
Translated from Greek - the birth of a baby, the main purpose of this vitamin. Obtained by distillation of vegetable oils, fat-soluble, but can be stored in the body for some time.
Contained in vegetable oils, legumes, cabbage, berries, sunflower seeds and fruit seeds.
Benefit:
Participation in reproduction;
Antioxidant (antioxidant), cleans organs from free radicals;
Affects the work of muscles;
Prevention of atherosclerosis;
Contributes to the normalization of cardiac activity;
Positive effect on red blood cells;
Helps the work of the glands (thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands);
Improves performance immune system;
Reduces the likelihood of cataracts;
Removes the effects of fatigue.
Enemies: O2, iron, chlorine, heat treatment destroy the vitamin.
Friends: selenium, digestibility depends on their interaction.
VITAMINH (biotin)
Sulfur and nitrogen are the necessary components of this compound
Contained in the liver, eggs, but the protein of a raw egg binds the vitamin, the body does not receive it, it is fat soluble.
Benefit:
Participates in protein, carbohydrate, fat metabolism;
Getting energy by man
Normalizes the functioning of the intestines, stomach, pancreas;
Improves the function of enzyme systems;
Calms the nerves;
Improves the functioning of the skin and restores it;
Reduces pain.
Enemies: Raw egg white, heat treatment, alcohol, some drugs.
Friends: activated in the presence of magnesium, does not oxidize in air.
VITAMINTO
fat soluble chemical element two forms.
Contained in pumpkin, green leaves of vegetables, tomatoes, soy, produced in the intestines.
Benefit:
Participates in the processes associated with blood clotting;
Reduces internal bleeding;
Helps heal wounds faster
It is necessary that calcium is better absorbed by bone tissue.
Enemies: all kinds of radiation (radiation, x-rays), certain drugs, bad ecology.
VITAMINN (lipoic, thioctic acid)
It is most active if it is integrated into the protein chain.
It is difficult to name foods that lack the vitamin, but sometimes it is inactive.
Benefit:
Participates in processes associated with the oxidation of some substances and the reduction of others;
Contributes to the normalization of metabolism;
Helps to provide the body with energy;
Protects the body from its toxins.
Friends: goes well with all B vitamins.
VITIMINP (rutin, citrine)
Bioflavonoids.
Found in citrus fruits, berries, buckwheat, lettuce, caffeinated drinks.
Benefit:
Strengthens blood vessels, promotes their better permeability;
Positive effect on the thyroid gland;
Promotes the production of pure adrenaline;
Helps the body resist infections.
Enemies: oxygen, light rays, food processing.
Friends: goes well with ascorbic acid.
VITAMINPP (nicotinic acid)
Water soluble, derived from a specific amino acid (tryptophan).
Contained in beans, peas, bran bread, white meat, potatoes, prunes.
Benefit:
Participates in metabolism;
Promotes saturation of cells with oxygen;
Improves the functioning of blood vessels and the heart;
Improves blood supply to the brain;
Normalizes the condition of the mucous membranes and skin;
Favorably affects digestion;
Strengthens the eye muscles;
Normalizes blood pressure.
Enemies: heat treatment, acetic acid.
Monotonousnutrition with a high content of refined substances, heat treatment of all products in order to disinfect them leads to a lack of vitamins, which always affects well-being, fatigue appears, and sometimes dizziness. In stressful situations, sports, and diseases, the consumption of vitamins increases. As a rule, most people begin to take vitamin complexes, regardless of the needs of the body. And you can normalize the work with a healthy diet. After all, this term means not only food as such, but also ways of processing products, their storage. Thanks to this, vitamins are maximally preserved in food.
The human body is not able to function properly without vitamins.
A person of any age will feel a lack or excess of vitamins on their own well-being. Vitamin deficiency in the body can lead to constant hunger and obesity. This is due to malnutrition, because along with a decrease in caloric content, the intake of the right amount of vitamins also decreases. This means that in order to get them, the body will begin to require more and more food.
In this article, we will pay special attention to such essential B vitamins for health.

The role of B vitamins is difficult to overestimate, as they are involved in many processes in our body. Each vitamin B of the group performs its vital mission for a person. Let's get acquainted with the main elements of group B.
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
The first discovered element from group B. Despite the fact that the intestinal microflora synthesizes this element, the body needs to replenish it daily.
The function of thiamine:
- Improves metabolism: produces energy, helps to digest proteins;
- Helps the nervous system to function properly, produces a special substance that is responsible for the functioning of the brain, improves the tone of the heart, stomach and intestinal muscles;
- Participates in the copying of genes transmitted to cells in the process of division.
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin)
This yellow-orange substance is able to be synthesized in the intestine. His role is also indispensable:
- Promotes the synthesis of nerve cells, supporting the functioning of brain neurotransmitters;
- Helps to mature erythrocytes and assimilate iron;
- Acts as a regulator in the functioning of the adrenal glands;
- Protects the eyes from ultraviolet radiation;
- Helps shape the skin and mucous membranes.

Vitamin B3 - nicotinic acid
Presented as a white powder, soluble in water. Niacin is more tolerant of heat, ultraviolet light, alkaline substances and air. It is produced by the body as a result of amino acid conversion.
Function in the body:
- Helps to synthesize enzymes, digest proteins, fats and carbohydrates, release energy and even improves cholesterol metabolism;
- Participates in the production of various hormones;
- Eliminates at the genetic level the problems that result from the influence of viruses and drugs on cells.
Vitamin B5 - pantothenic acid
Like his "classmates" we will dissolve in water. It is produced in the intestinal environment with the help of symbiotic bacteria. If B5 is heated in an acid-base environment, it will collapse.
The role of pantothene:
- Helps to release food energy;
- Regulates the work of the central nervous system, producing for this a special enzyme - acetylcholine.
- Protects the immune system, helps to synthesize antibodies and heal wounds;
- Promotes the efficient functioning of the adrenal glands, helps to produce a special hormone responsible for the response to stress.
- Forms healthy red blood cells and helps synthesize hemoglobin.

Vitamin B6 - pyridoxine
Consists of a whole group of water-soluble compounds. They are resistant to high temperatures and oxygen, but hardly tolerate light. They can be synthesized by symbiotic microorganisms in the human intestine, but they are easily harmed by antibiotics.
The role of pyridoxine:
- Supports almost all metabolic processes of the body, controlling the activity of sixty enzymes;
- It is a synthesizer of special fat-containing elements that regulate the activity of the heart and blood vessels.
- Stimulates cell division and promotes the formation of antibodies, thereby supporting the health of the immune system;
- Supports the stable functioning of the central nervous system;
- Helps form genetic material, absorbs vitamin B12.
Vitamin B7 - Biotin
Soluble in water, has sulfur in its composition, does not lose strength under the influence of high temperatures. Produced by symbiotic bacteria living in the intestinal environment.
Functions of vitamin B7:
- Starts digestive enzymes;
- Is an accomplice of metabolic processes;
- Helps fight diabetes
- Improves skin condition.
Vitamin B9 - folic acid
Water-soluble element of bright yellow color. The form of the vitamin is quite stable. Synthesized by healthy intestinal microflora.
Functions of folic acid:
- Needed for the formation of RNA, DNA;
- Participates in protein metabolism;
- It is a synthesizer of healthy erythrocytes and leukocytes.

Vitamin B 10 - para-aminobenzoic acid, PABA
This vitamin-like white substance, unlike its vitamin counterparts, dissolves in alcohol and ethereal liquids. The element is chemically stable and able to withstand boiling in an acid-base environment.
The functions of the B 10 are the most diverse:
- is responsible for the normal pigmentation of the nail plates and hairline;
- stabilizes the growth of beneficial intestinal microflora;
- is the main material that helps to develop vitamin B10 for the intestines;
- promotes the production of protein and red blood cells;
normalizes the functioning of the thyroid gland;
improves digestive processes; - helps to increase the production of breast milk;
- helps to absorb some vitamins;
is a tool that helps prevent the formation of blood clots; - supports the health of male sexual function.
Vitamin B12 - cyanocobalamin

This item is bright red. It is temperature resistant. If it is exposed to oxygen, ultraviolet, alkaline and acidic environments, it loses its properties. Most of the vitamin cyanocobalamin is in the liver, some is produced by the intestines.
Functions of B12:
- Releases food energy;
- Indispensable for rapid cell division;
- Forms a protective nerve sheath.
- Boosts immunity by helping to mature red blood cells.
- Reduces the proportion of cholesterol in the blood, helps the liver to work.
Daily rate
Based on the considered role of vitamins of the B group, it can be concluded that these substances support the stable functioning of the body. A person throughout his life, if he wants to remain healthy, it is necessary to monitor the sufficient intake of the considered vitamins. A table containing data on the required daily intake of vitamin B in the diet from a person’s birth to old age will help with this.

It is important to note that the body, under the toxic effects of heavy metals, nicotine and alcohol, needs to increase the rate of vitamin B1 to 5 mg. This also applies to cases where a person has been stressed for a long time.
With the wrong diet, when carbohydrates predominate in food and alcohol is often consumed, it is also better to increase the dose of vitamin B1. On the contrary, it is necessary to reduce the rate of this element if you are a fan of fatty or protein foods.
It is always necessary to satisfy the daily requirement of vitamin B, because its deficiency, as well as an excess in the diet, leads to problems in the functioning of important organs.
In food

It is possible to replenish the supply of B vitamins with the help of certain foods. Knowing the daily norm of a certain vitamin and the products where it is contained, it is not difficult to strengthen your health, and at the same time eat delicious food. The second table contains food products for each considered category of elements in group B.

IMPORTANT: Subjecting food to heat treatment, boiling, refining, we force B group vitamins to lose their beneficial features or completely collapse. And under the influence of alcohol, coffee, tobacco, citric acid, citric acid and products with their composition thiamine almost completely loses its ability to be absorbed into the body.
deficit

But more often than not, what we eat now does not benefit our health. People living in big cities suffer from beriberi. Mired in the hustle and bustle of offices, in eternal problems, they live on the run and eat, as a rule, also not quite healthy food on the run. And then they suddenly notice that not everything is going smoothly with their health.
B group vitamins are insidious by their long silence about their deficiency. This group does not have the habit of "making reserves" in the body and you always need to be on the alert with them. Lack of vitamins can manifest itself in various ailments.
Especially a person needs vitamins during superpower loads, stress, during pregnancy and lactation.
It is very important to provide children with vitamins, thereby protecting them from infections and negative environmental influences.

Vitamins should not be forgotten by the elderly, whose disturbed metabolic process leads to beriberi or hypovitaminosis. Due to age-related cellular changes, absorption and utilization disorders, they cause vitamin deficiency even if all daily norms are observed.
Victims of predetermined beauty standards - lovers of diets - fall into the risk group.
Strengthening and maintaining health and vitality is quite a feasible task for any person. You just need to be attentive to your body. Treat yourself to vitamins more often, but do not overdo it. Be healthy!

Anton Palaznikov
Gastroenterologist, therapist
Work experience more than 7 years.
Professional skills: diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary system.
Content:
The most basic representatives of B vitamins. Why are they needed, their functions, daily dosage, content in products.
B vitamins are the most powerful energy sources that the cells of the body and, first of all, the brain need. For this reason, they are considered the main ones in the issue of normalizing the work of the central nervous system, key organs and body systems.
What types of these elements exist? What are their features? What is the correct dosage?
Thiamine (B1)
Based on the discovery time, then thiamine in the group of B vitamins can rightly be called the leader. Its feature is water solubility. Because of the inability to store thiamine, it must be present in the daily diet. At the same time, it comes in two ways - with food and is produced in the body (in the intestines).
When planning a diet, it is worth considering that during the cooking process, 25 percent of the element is destroyed by heat. There are two main negative factors - boiling and contact with metals. In addition, the amount of thiamine decreases during the refining of products made from grains - muesli, cereals, and so on. Also, vitamin B1 is worse absorbed under the influence of the following factors:
- alcohol;
- tobacco;
- products containing salts (carbonic, citric);
- coffee and so on.
Thiamine acts on the body as follows:
- Improves metabolic processes. Studies have shown that the element is involved in the production of energy, the exchange of proteins, amino acids and carbohydrates entering the body.
- Normalizes the functioning of the nervous system, activates the brain. Due to its ability to act on the central nervous system and the activity of the “gray matter”, thiamine is often called the “vitamin of good spirits”. The main plus is its participation in the synthesis of acetylcholine, which is a powerful neurotransmitter. The latter improves memory, supports the heart muscle, and normalizes the functioning of the intestines and stomach.
- Transfers genetic information. One of the main tasks of the element is considered to be participation in the transfer of genetic data at the intercellular level.
Thiamine is found in the following foods:
- almond;
- Red beetroot;
- cabbage;
- potato;
- carrot;
- apricots;
- rose hip;
- beans and so on.
Dosage:
- adults - 1-2.5 mg(depending on load and age);
- children - 0.5-2 mg;
- in special situations (stress, nicotine or heavy metal poisoning) - 4.5-5 mg.
With a lack of thiamine in the diet, the risk of its deficiency increases. The main reason for this is a monotonous diet, increased consumption of sweets and carbohydrate-containing foods. B1 deficiency often affects people who abuse alcohol.
Deficiency signs:
- disruption of the central nervous system - headaches, irritability, paralysis;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract - nausea, pain in the abdomen, problems with the stool;
- heart problems - tachycardia, increased swelling, pain in the heart.
Consequences of long-term vitamin deficiency:
- decrease in the rate of protein production;
- disorder of the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract;
- tachycardia, pressure drop and so on.

Riboflavin (B2)
An equally important element for the body is riboflavin or B2, which is a water-soluble substance that has a yellowish-orange color. It enters the body with food and is produced in the large intestine.
Factors contributing to the destruction of the vitamin are as follows:
- UV rays;
- heating;
- defrosting.
Item action:
- participates in the normalization of the work of CNS cells;
- protects the retina from UV rays;
- activates the production of red blood cells;
- accelerates the production of iron;
- regulates the work of the adrenal glands;
- has a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin, rejuvenates them.

Riboflavin is found in:
- vegetable origin: green peas, rose hips, wheat bread, cereals (oatmeal, buckwheat).
- Animal origin: liver, kidney, meat, fish and eggs. The advantage of these products is better digestibility.
Daily rate:
- for adults - 2-6 mg;
- for children - 1-3 mg.
B2 deficiency manifests itself as follows:
- dermatitis of the skin of the face and chest;
- inflammatory processes occurring in the area of the lips and oral cavity;
- loss of appetite;
- headache;
- decrease in performance.
An excess of vitamins B1 and B2 has no significant consequences.
Niacin (B3)
Considering the B vitamins and their effect on the body, special attention should be paid to niacin. It has a powder form and is white in color, belongs to the category of water-soluble.
B3 is considered the most stable among other members of the group due to its ability to withstand heat, air, alkalis and UV rays.
Its functions:
- Normalization of metabolic processes, improvement of the assimilation of the main elements for the body (proteins, fats and carbohydrates). The action of B3 is also aimed at normalizing cholesterol levels.
- Participation in the production of various hormones - thyroxine, cortisone, insulin and other vital substances.
- Help in repairing damage at the genetic level caused by the action of viruses or drugs.
- Support for the work of the central nervous system, improvement of brain activity.
- Normalization of pressure (arterial, venous).
- Stimulation of the production of red blood cells.
The vitamin in question is found in:
- animal products- fish, lean meat, kidneys, liver.
- herbal products- garlic, peas, parsley, legumes, buckwheat and others.

Dosage of niacin:
- adults - 20 mg(limit level - 60 mg);
- children - 5 mg(limit level - 20 mg).
Deficiency is manifested by a number of unpleasant signs:
- insomnia;
- blanching of the hands and lips;
- excessive weakness, fatigue;
- memory impairment;
- dry skin;
- distortion of taste sensations.
Prolonged vitamin deficiency leads to the following consequences:
- pathologies associated with the gastrointestinal tract;
- skin problems;
- malfunctions of the central nervous system;
- the appearance of a deficiency of other representatives of group B.

Pantothenic acid (B5)
Vitamin B5 is a water-soluble element that is part of many foods. Partially produced in the intestines. Destroyed by alkali and acid.
- aid in the breakdown of fats and carbohydrates;
- normalization of the central nervous system;
- acceleration of wound healing, strengthening of the immune system;
- normalization of the adrenal glands;
- involved in the production of hemoglobin.
B5 is found in the following products:
- vegetable origin- whole grains, hazelnuts, green vegetables, bran, beans, mushrooms.
- Animal origin- eggs, kidneys, liver, dairy products.
Dosage - 5-15 mcg per day.
Deficiency leads to the following problems:
- sleep disturbance;
- failures in metabolic processes;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system and heart.

Pyridoxine (B6)
This element belongs to the category of water-soluble, comes with food. Pyridoxine is synthesized in small amounts in the intestine. During cooking, some of the substance is lost.
The action is as follows:
- Normalization of metabolic processes, assistance in the absorption of proteins and fats.
- Participation in the synthesis of prostaglandins - fat-soluble elements that regulate the functioning of the heart muscle and normalize the level of pressure.
- Strengthening the immune system, the formation of antibodies.
- Normalization of the functioning of the central nervous system and brain function, acceleration of mental activity, improvement of mood. It should be noted that the level of B6 in the "gray matter" exceeds that in the blood by 30-50 times.
- Improving the condition of the skin, preventing skin aging.
- Other functions - assistance in the synthesis of red blood cells and hormones, the full absorption of B12.
Vitamin is found in the following components of our diet:
- bird;
- pork;
- beef liver;
- buckwheat;
- potato;
- strawberry;
- cherries;
- lemon;
- pomegranate;
- oranges.

Element deficiency leads to the following problems:
- malfunctions of the central nervous system (drowsiness, excessive irritability);
- deterioration of the immune system;
- skin problems;
- anemia (most often seen in children).
Vitamin is most in demand:
- infants;
- pregnant women;
- patients with atherosclerosis, chronic diseases, polyarthritis;
- in the process of taking contraceptives;
- with prolonged use of antibiotics.

Biotin (B7)
Vitamin B7 also belongs to the category of water-soluble. Its features are the content of sulfur in the composition, resistance to processing during the preparation process. It enters the body with food and is partially produced in the intestines.
- activation of digestive enzymes;
- improvement of metabolic processes, normalization of energy metabolism;
- help with diabetes
- improvement of the condition of the skin;
- normalization of the digestive tract due to the production of digestive enzymes.
Biotin is found in many foods:
- Brewer's yeast;
- almond;
- peas;
- walnuts;
- tuna;
- parsley;
- kidneys;
- milk;
- apples;
- bananas.
Deficiency leads to the following problems:
- anemia;
- exacerbation of the sensitivity of the skin;
- cholesterolemia;
- fragility of the nail plates, hair loss;
- inflammation of the skin.

Folic acid (B9)
Vitamin B9 has a bright yellow color and is highly soluble in water. It enters the body in two ways - synthesized in the intestines or with food. A small supply of the element (for 3-6 months) is also present in the human liver.
The action of folic acid is aimed at solving a number of problems:
- participation in protein metabolism;
- help in cell division, support of the genetic code;
- normalization of the nervous system;
- synthesis of vital blood elements - leukocytes and erythrocytes.
It contains:
- plant sources- legumes, potatoes, tomatoes, lettuce, rye, beans, asparagus.
- Animal sources- egg yolk.
Many people do not know what B vitamins affect, which is why they do not adjust their diet. In case of folic acid Is it dangerous. Its deficiency can lead to the following consequences:
- blood diseases;
- violations in the development of the child during pregnancy (malformation, miscarriage);
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Dosage:
- average daily rate 400 mcg;
- marginal rate - 600 mcg.

Cyanocobalamin (B12)
Another needed by the body element - B12, which has a bright red color and is able to dissolve in water. It comes with food, but in a small amount it is also found in the body (3-5 mg). B12 activity is reduced by:
- oxygen;
- UV rays;
- acids and alkalis.
What is the function of this vitamin? Here it is worth highlighting the following actions:
- help in releasing energy from food;
- myelin formation, prevention of malfunctions in the central nervous system;
- normalization of blood clotting;
- participation in the production of nucleic acids;
- lowering cholesterol levels.
Dosage - 3-9 mcg.
The vitamin is found in:
- heart;
- fish;
- liver;
- sea kale;
- milk and dairy products.

Deficiency signs:
- constipation;
- weakness;
- loss of appetite;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- duodenal ulcer and stomach ulcer.
Results
Knowing which B vitamins and in what volume the body needs, it is easier to correctly prioritize, form a diet and eliminate many health problems.
- How to make a collapsible bow from skis with your own hands Do-it-yourself sports bow drawings
- PPR schedule of welding equipment sample
- Application and location
- Eight home production ideas on video
- Waste of materials in the production of asphalt mix
- Reliable waterproofing of the foundation with your own hands What tool to make the waterproofing of the foundation
- Altai anemone description
- Decorating and decorating flower pots with your own hands without leaving home
- Industrial lighting, its quantitative and qualitative characteristics
- The use of liquid glass for waterproofing How to apply liquid glass to the foundation
- Do-it-yourself birdhouse made of wood: drawings, materials, decor and installation How to make a birdhouse for birds from wood
- Do-it-yourself bed-house for children (6 photos) Drawing of a children's bed of a house
- Disinfection of water by chlorination
- How to make lamps from LED strips Powerful do-it-yourself LED lamp 220v
- Autumn decoration of the group in kindergarten Decoration of the ceiling autumn in kindergarten
- Large New Year's vytynanka templates About decorating windows with an electric garland
- Projects of apartment buildings
- Precision Lost Wax Casting at Home: Technology, Advantages and Disadvantages Gypsum sand for aluminum casting
- Which socket to choose for the hob?
- Why does the trunk of an orchid turn yellow?